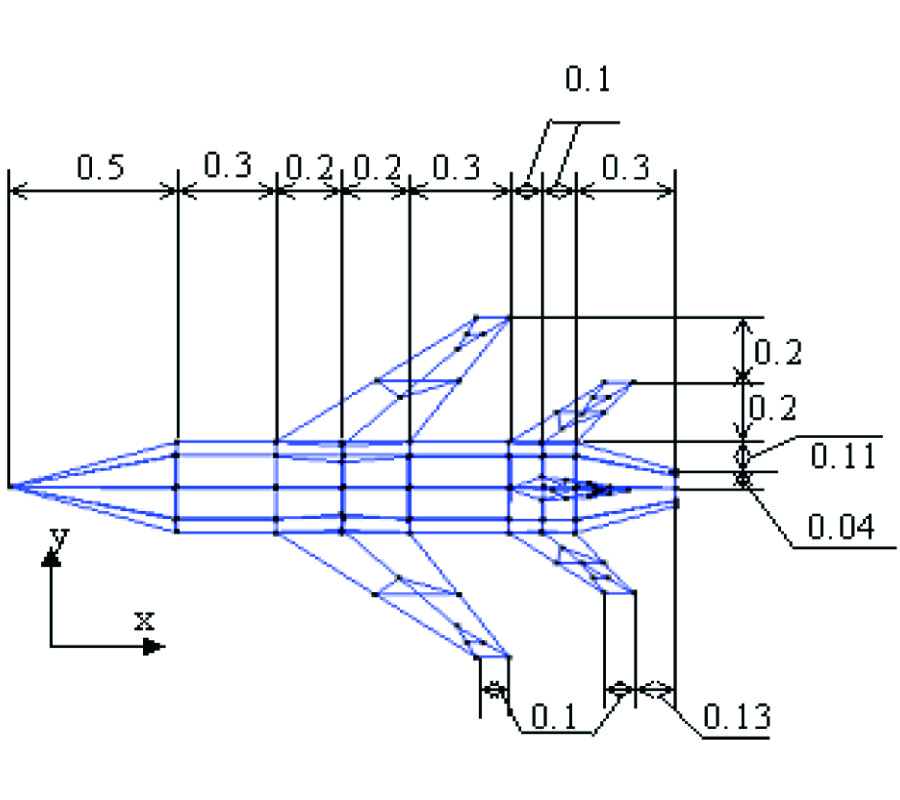
Fast Calculation of Wide-Band Responses of Complex Radar Targets
Shaogang Wang,
Xinpu Guan,
Dang-Wei Wang,
Xingyi Ma and
Yi Su
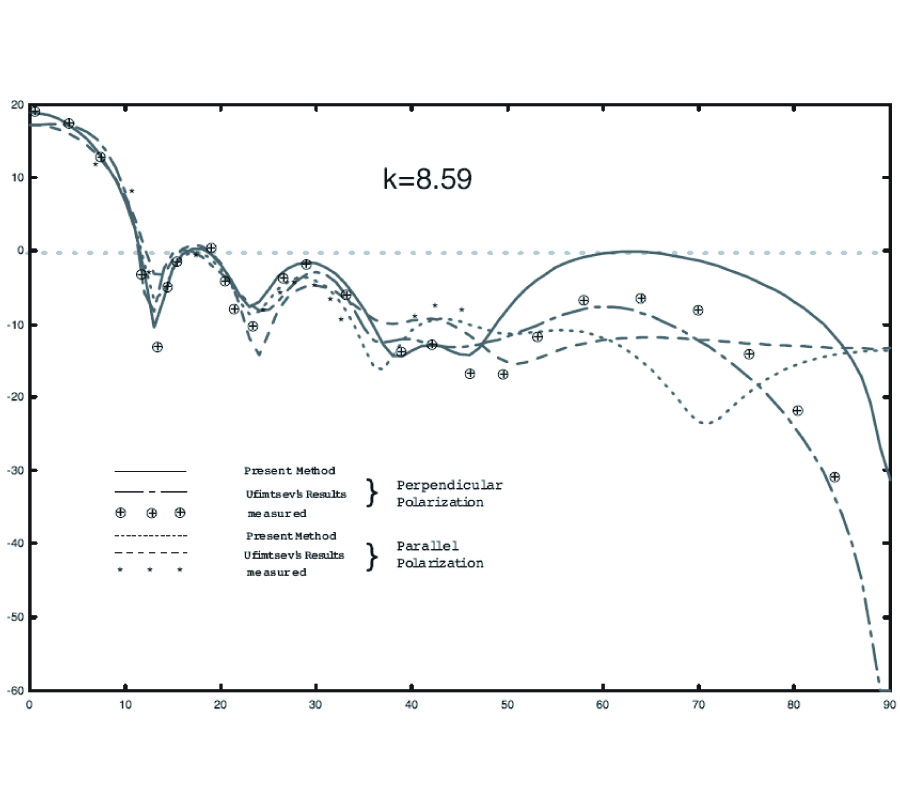
In this paper, a fast method is proposed to calculate wide- band frequency responses of complex radar targets on a personal computer. When frequencies are low, the frequency factor can be separated from space parameters by Chebyshev polynomial approximations of Green's function. Then, matrices from MoM at different frequencies can be rapidly filled, and monostatic RCS can be soon calculated. If frequencies are relatively high, a fast high-order MoM (HO-MoM), in which matrices products are in place of multi- dimension numerical integrations, is presented. That will reduce the CPU time requirement. Lastly, Numerical results are given for various structures and compared with other available data.