2013-02-04 Latest Published
By Yong Liu
Xiaohong Tang
Zhong Xun Zhang
XiaoLong Huang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 136, 765-773, 2013
Abstract
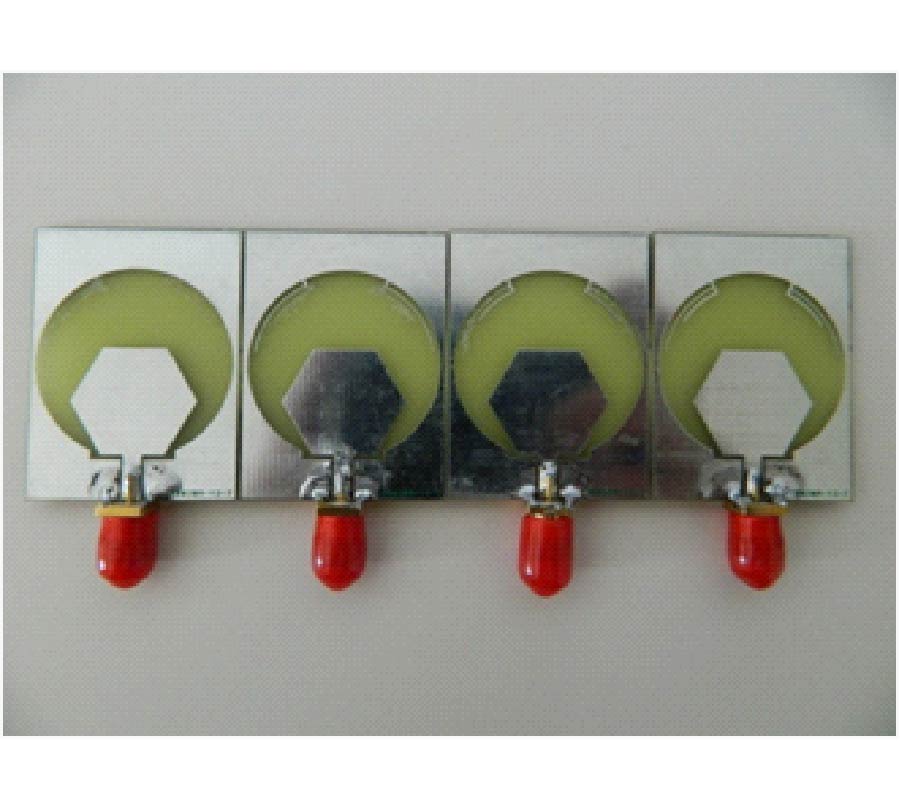
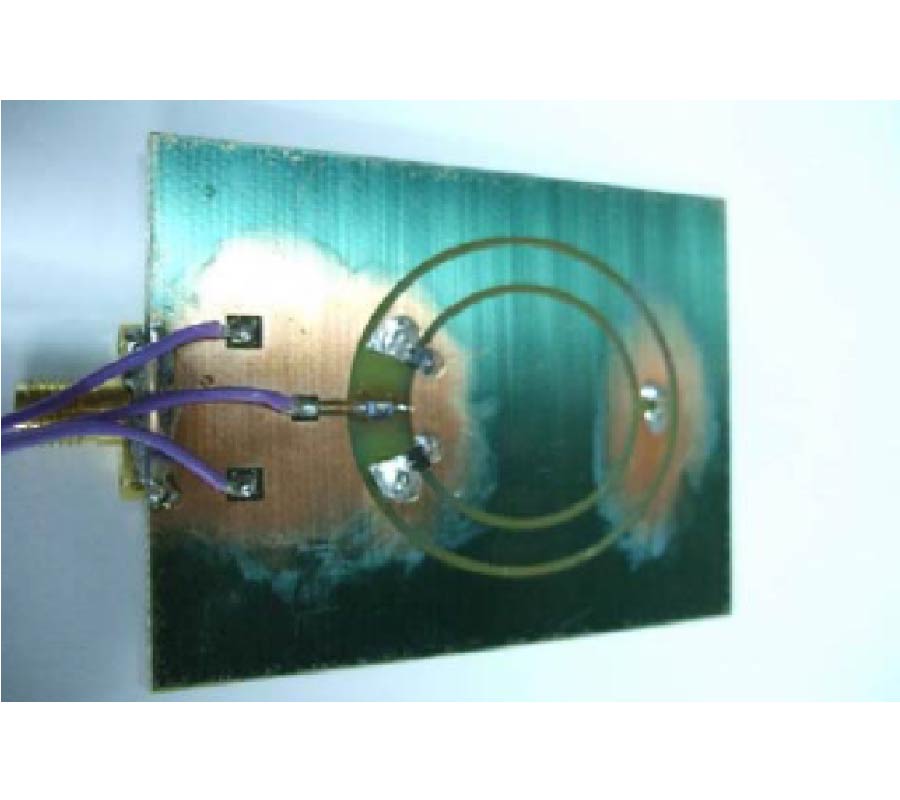
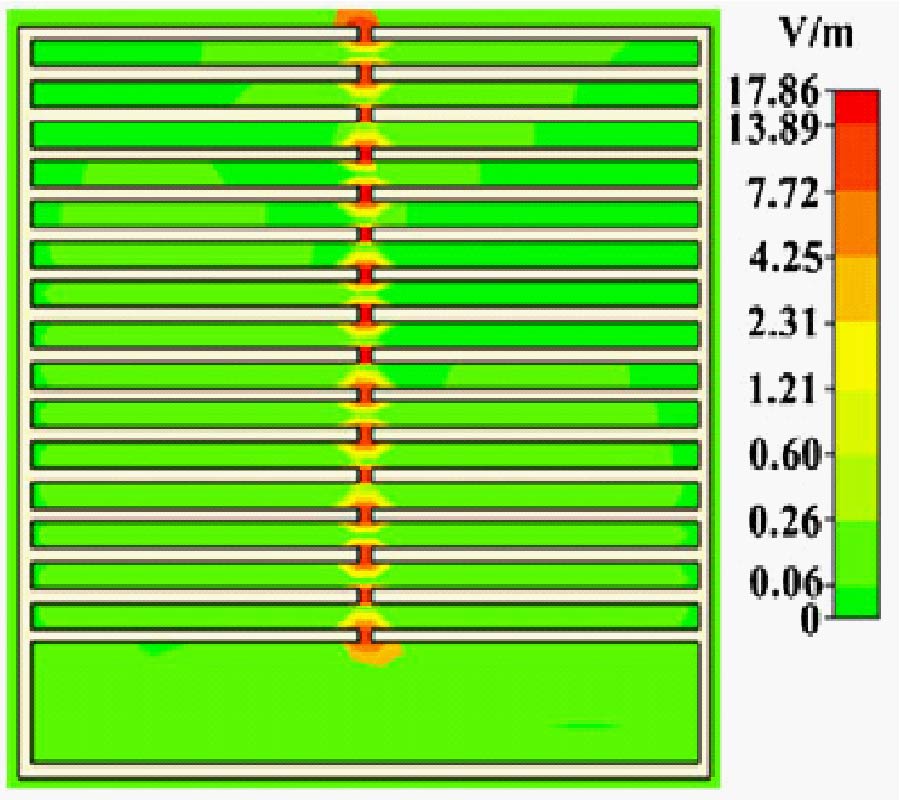
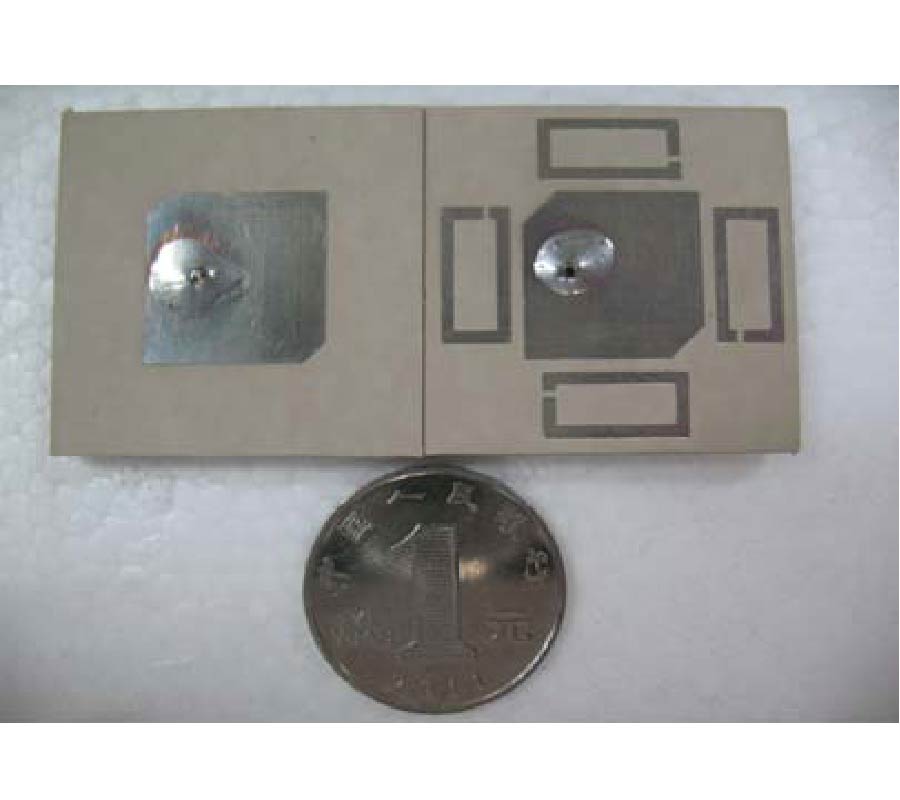
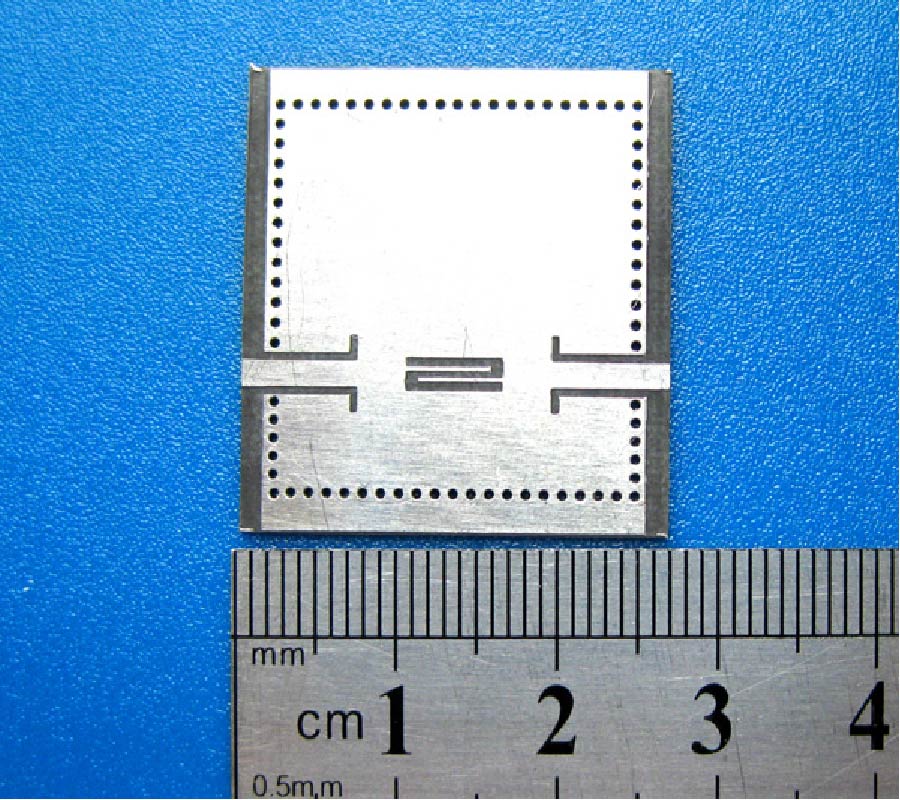
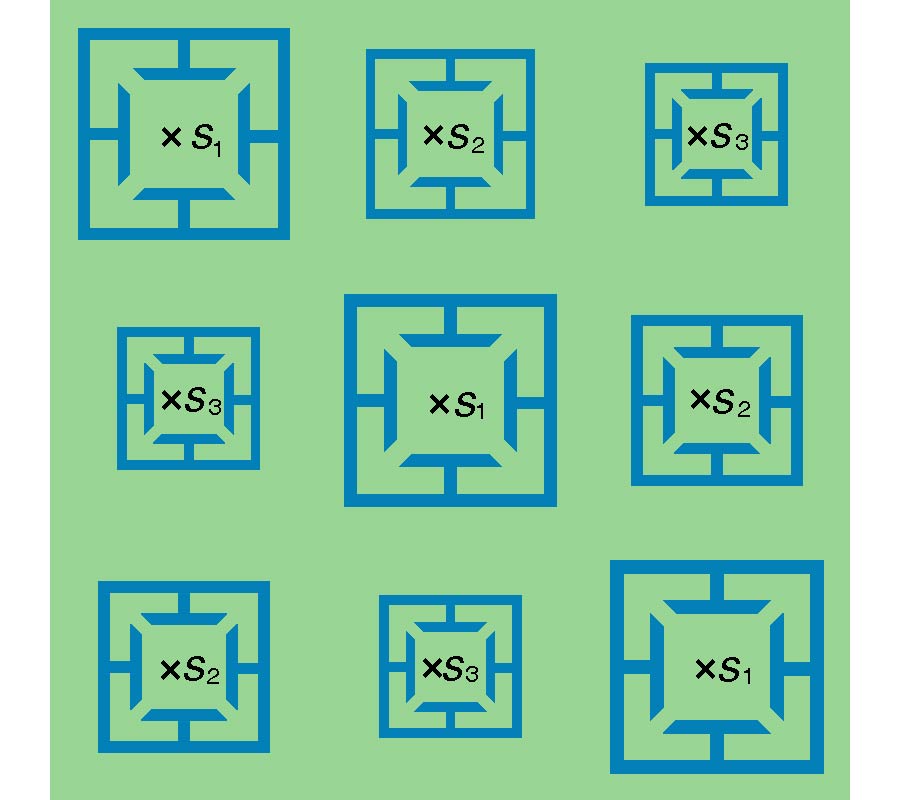
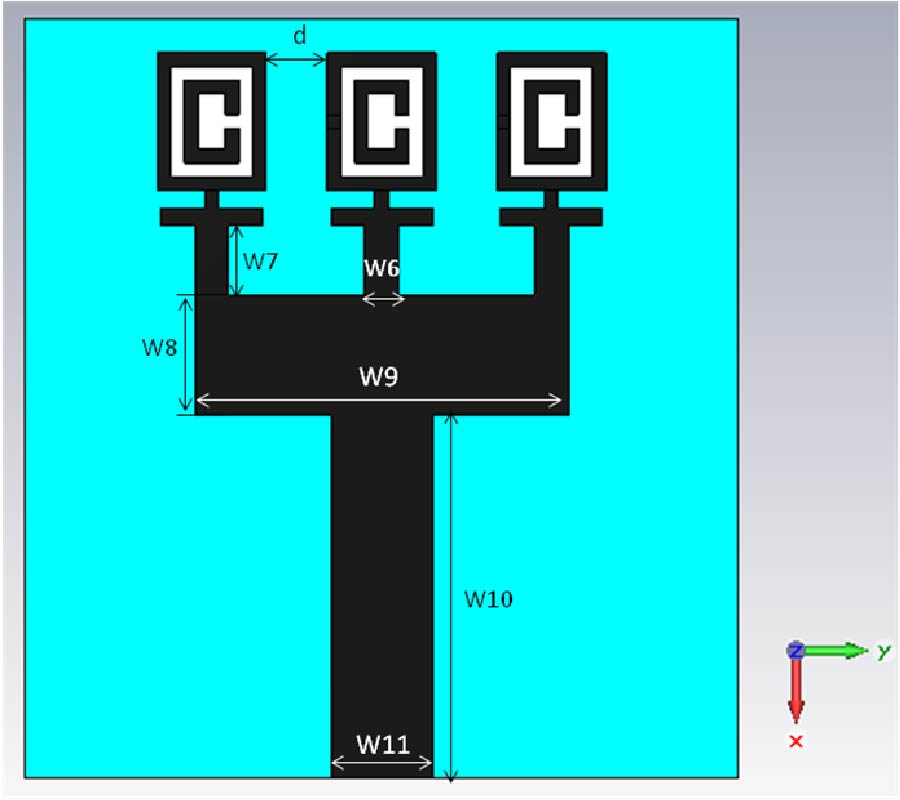
In this paper, a novel miniaturized nested split-ring resonator (SRR) structure is proposed. The nested SRR structure incorporates multiple split-ring resonators in a compact nested structure, and has more split gaps than the conventional SRR structure. Compared with conventional SRR, this nested SRR has better performance on miniaturization and high-Q value. To verify good characteristics of the proposed resonator structure, a novel resonator-embedded band-pass filter (BPF), which is constructed by four nested resonators, is designed. This novel BPF is very compact and has good in- and out-band performances. The proposed nested SRR unit cell has size of 0.04λg x 0.04λg(λg is the signal wavelength at the 2.4 GHz central frequency of the pass-band). Its stop-bands are extended 0.5~2 GHz at lower band and 2.7~5.4 GHz at upper band with a rejection level of higher than 20 dB, and its 1-dB pass-band is 2.2~2.55 GHz with 1.8 dB optimized insertion loss. The measured and simulated results are well complied with each other.