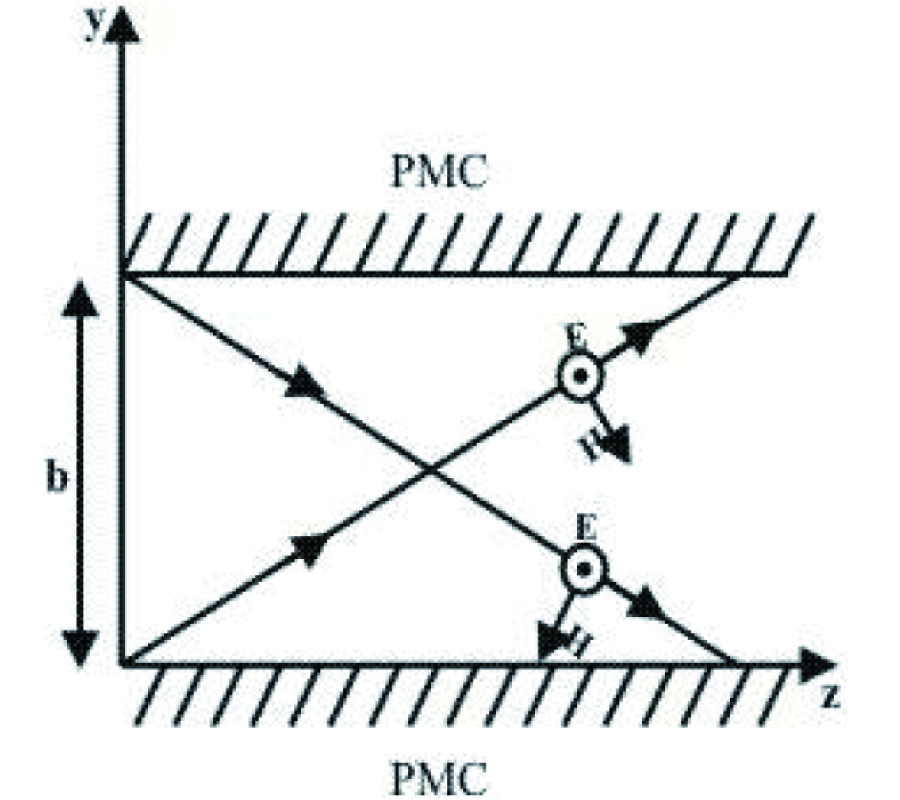
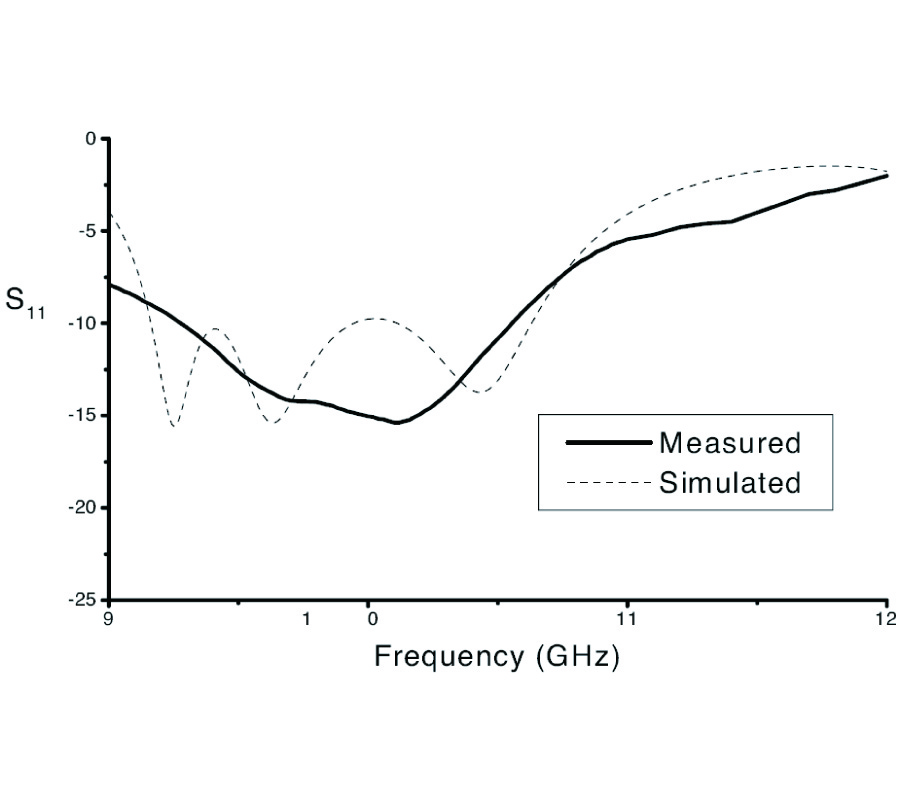
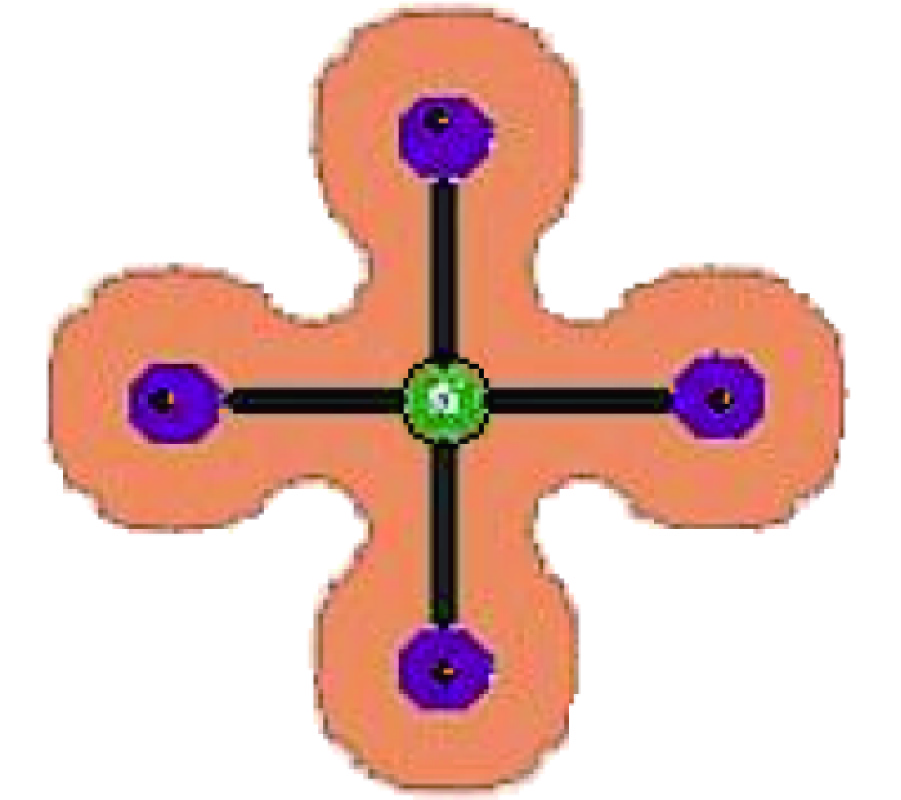
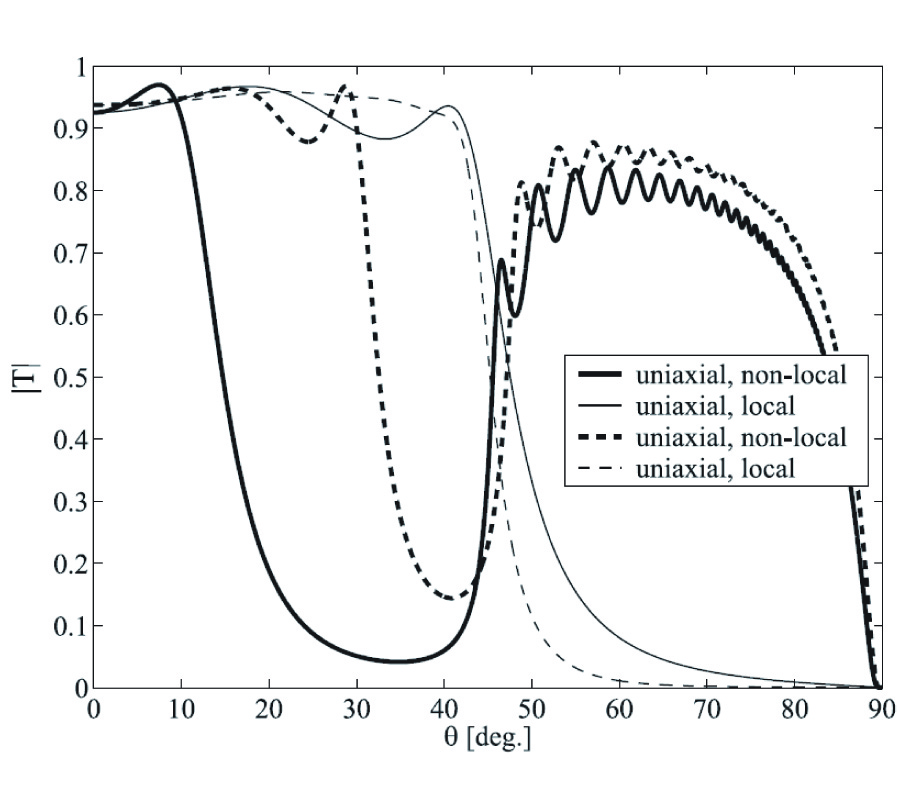
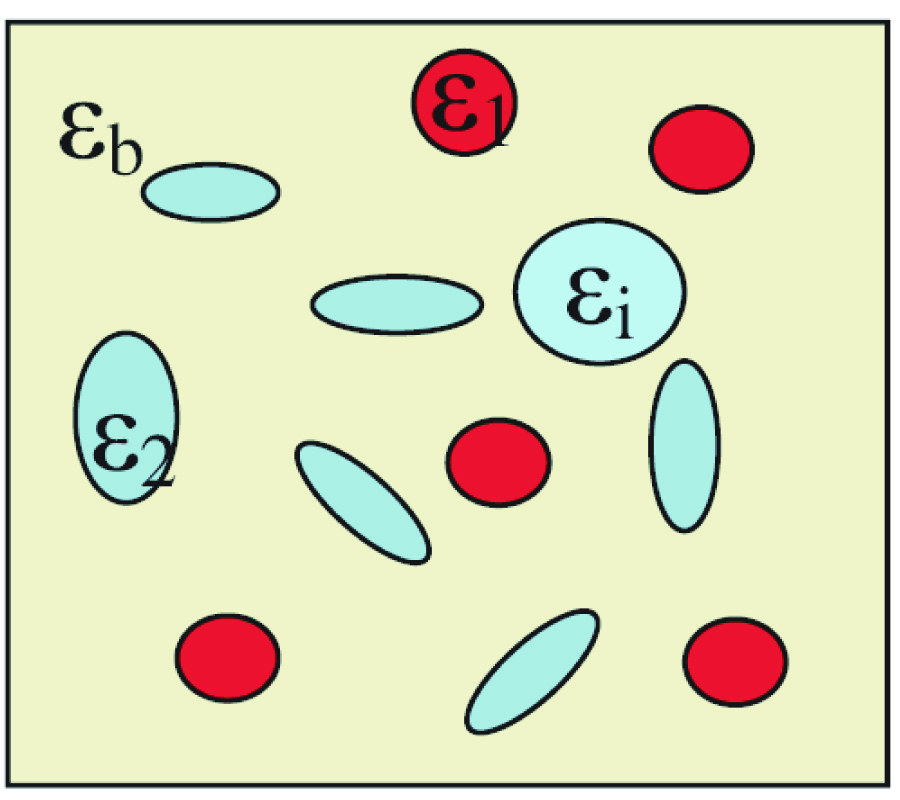
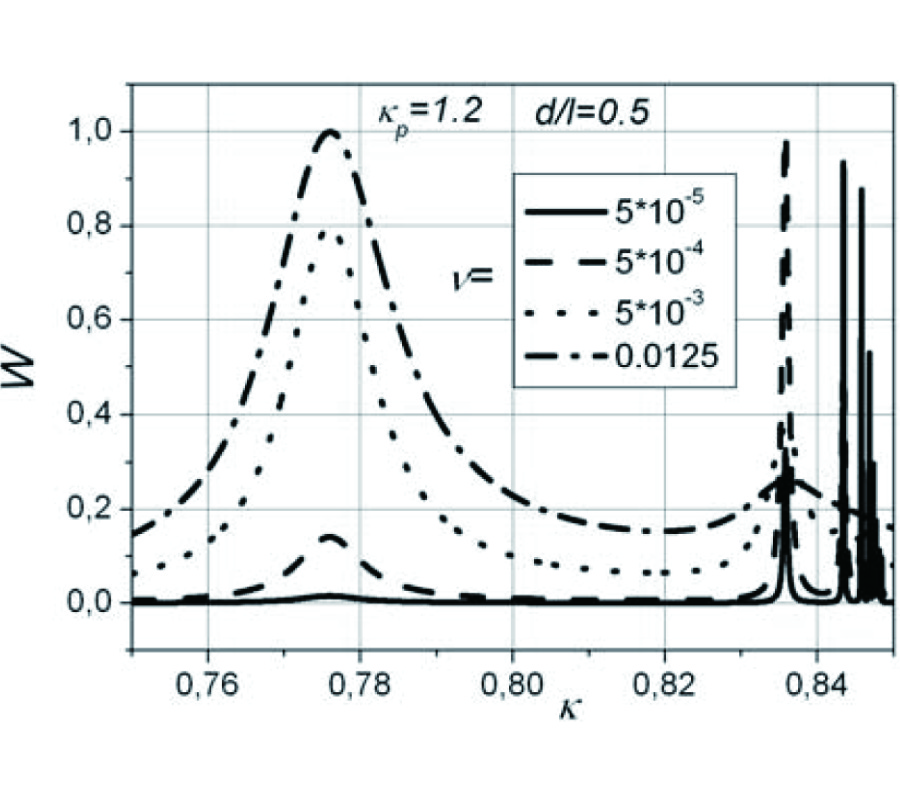
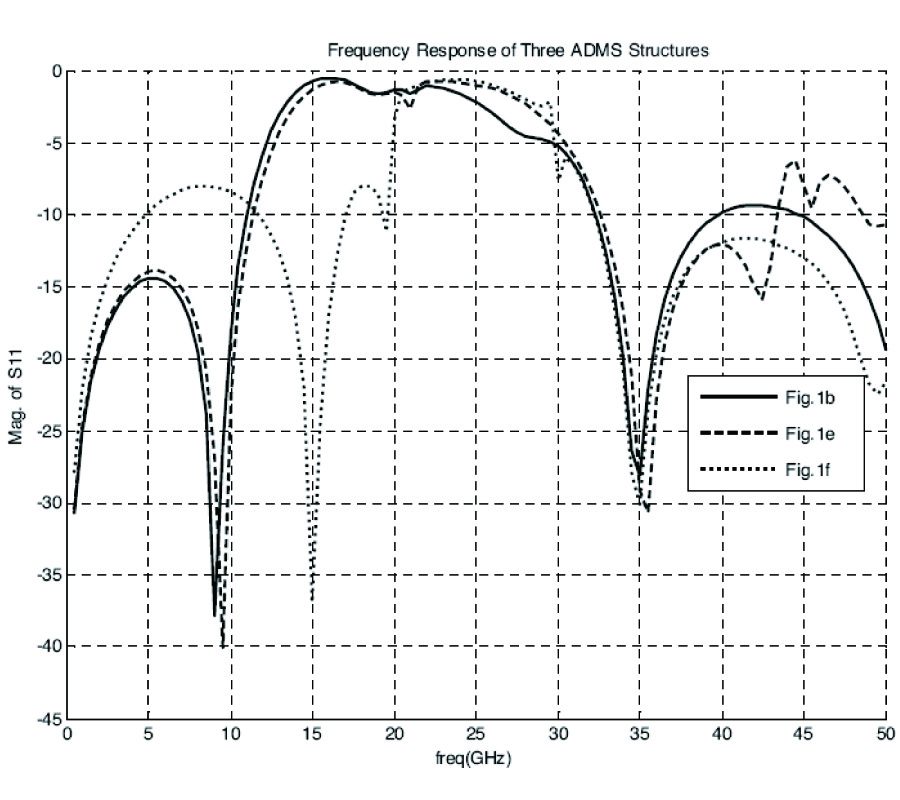
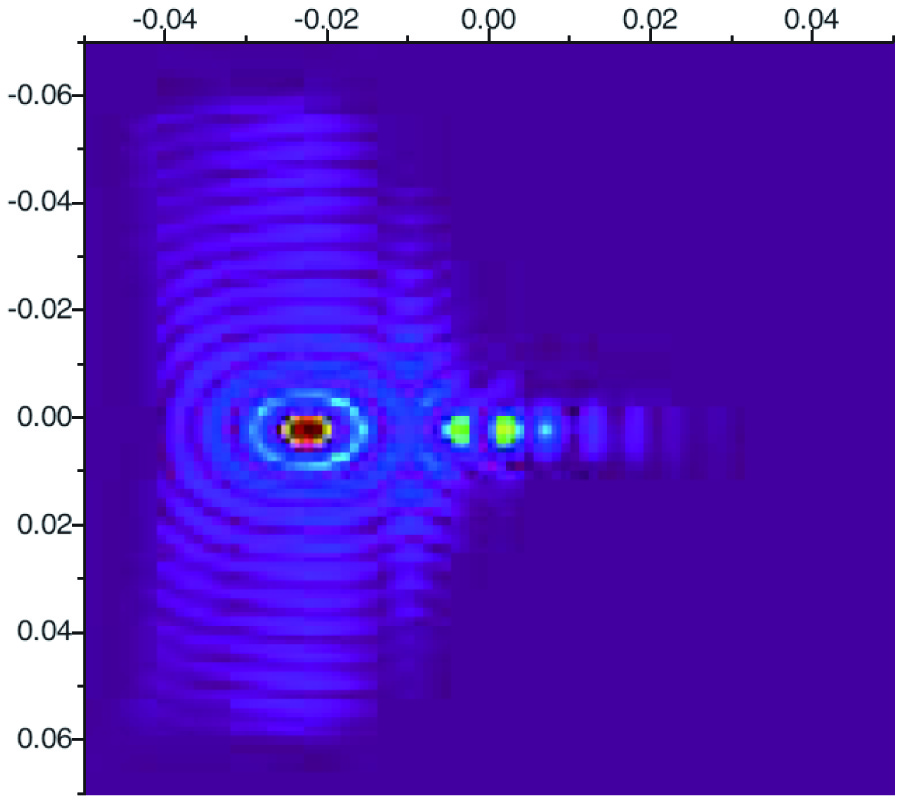
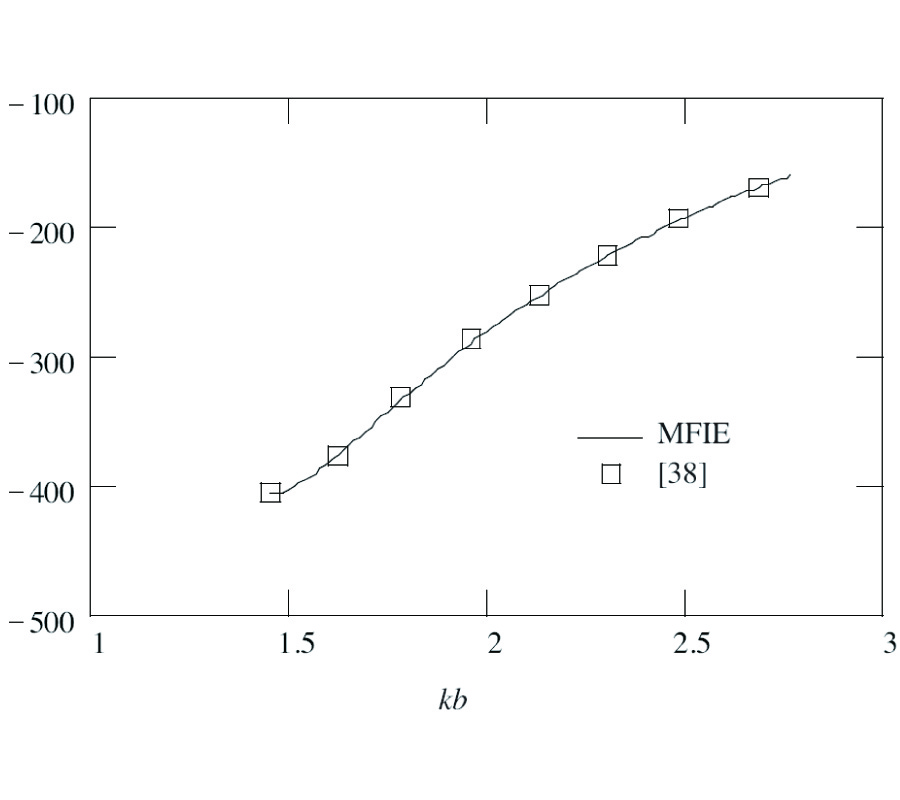
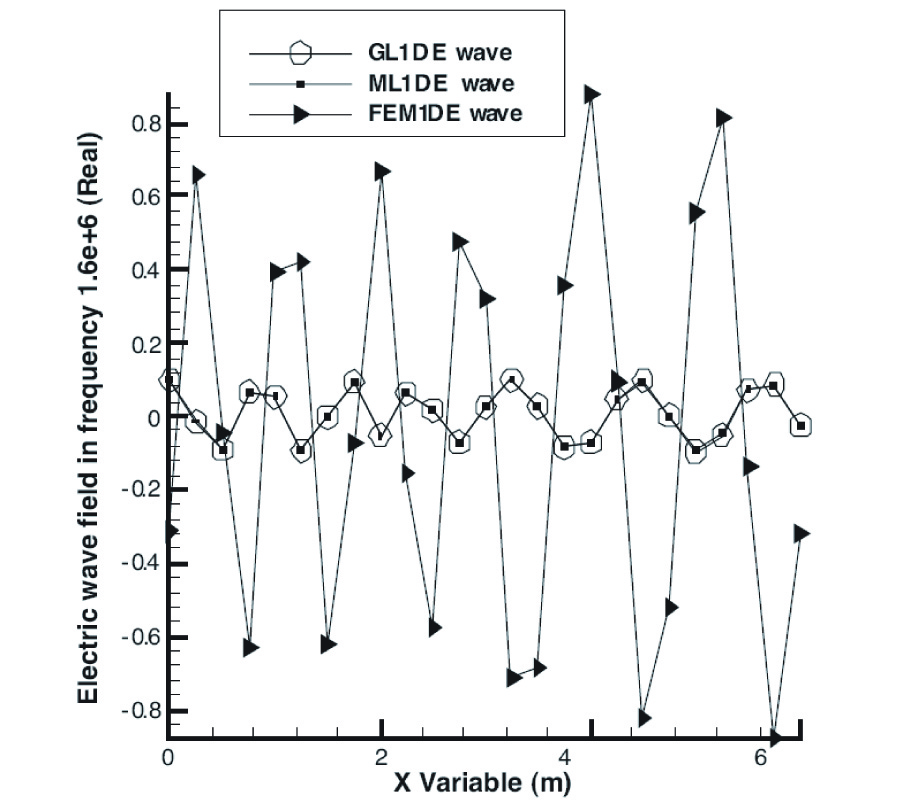
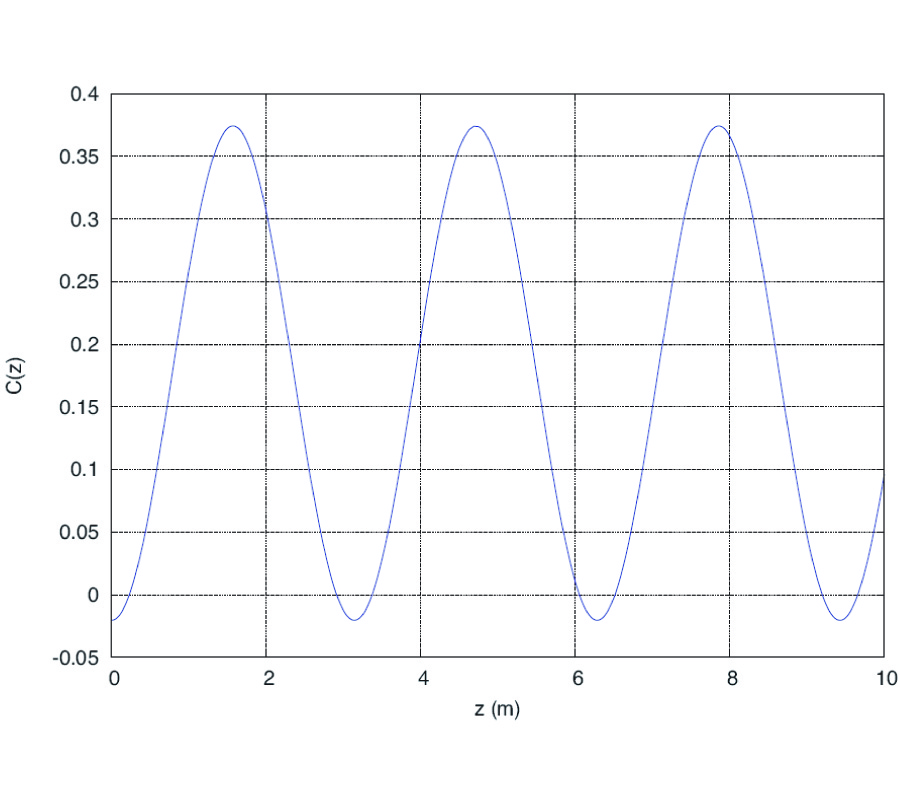
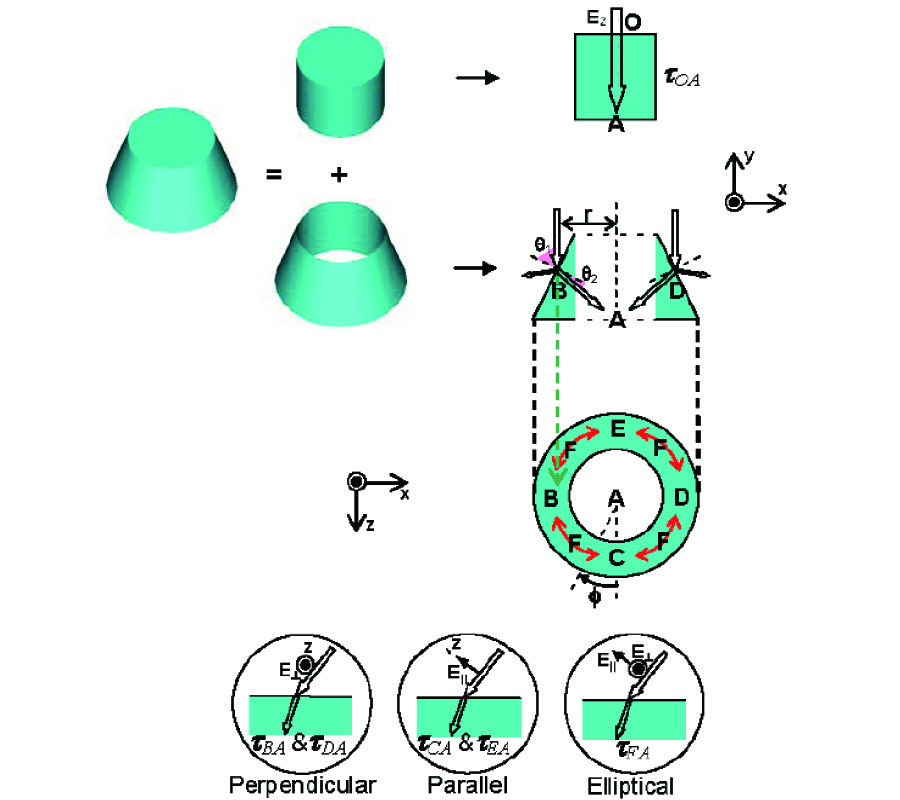
New Gl Method and Its Advantages for Resolving Historical Difficulties
Ganquan Xie,
Feng Xie,
Lee Xie and
Jianhua Li
Abstract-In this paper, we propose two types of new electromagnetic (EM) integral equation systems and their dual integral equation systems. Based on the EM integral equation systems, we propose a GL EM modeling and inversion algorithms. We make finite step iterations to exactly solve these integral equation systems or the EM and seismic differential integral equations in finite sub domains. The Global EM wave field is improved successively by the Local scattering EM wave field in the sub domains. Only 3 x 3 or 6 x 6 small matrices need to be solved in the GL method. There is no artificial boundary for infinite domain in the method; In the GL method, the cylindrical and spherical coordinate singularities are resolved; Our method combines the analytic and asymptotic method and numerical method. It is more accurate than FEM and FD method and Born likes approximation, the GL method is available for all frequencies and high contrast materials. Its solution has O(h2) convergent rate. If the Gaussian integrals are used, the field has O(h4) super convergence. The method is a high perform parallel algorithm with intrinsic self parallelization properties. The method has very simple scheme or no scheme or half scheme such that it has half mesh and no mesh. In the method, we can use both of Riemann and Lebesgue integral that induces a meshless method. We have developed software for 3D/2.5D EM, seismic, acoustic, flow dynamic, and QEM modeling and inversion.