A Survey of Various Frequency Domain Integral Equations for the Analysis of Scattering from Three-Dimensional Dielectric Objects
Baek-Ho Jung,
Tapan Kumar Sarkar and
Y.-S. Chung
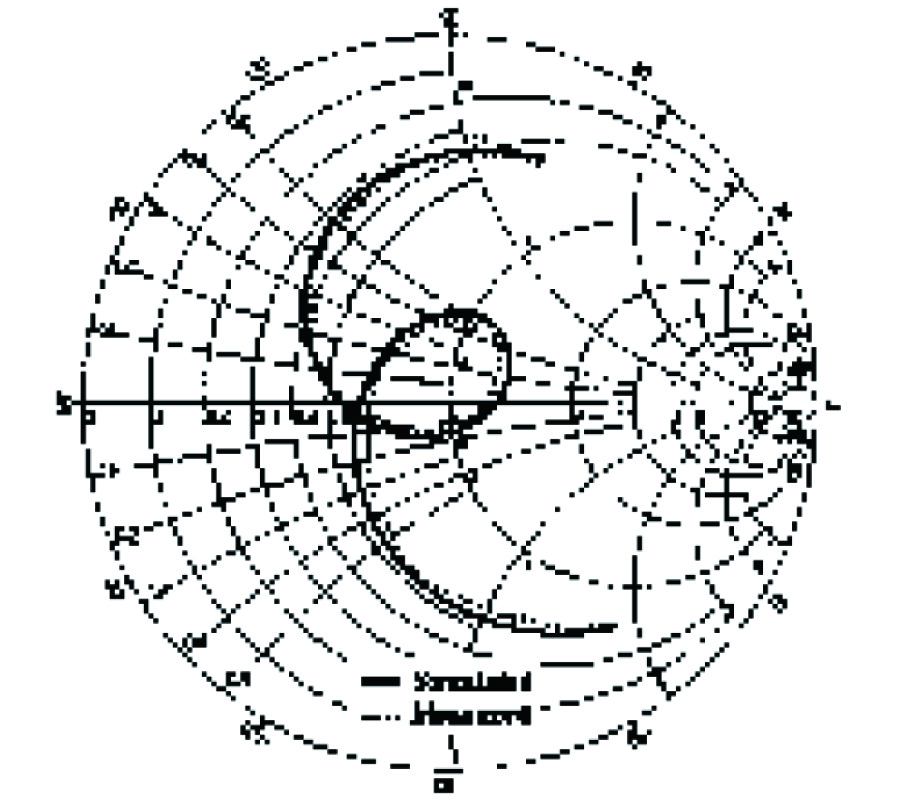
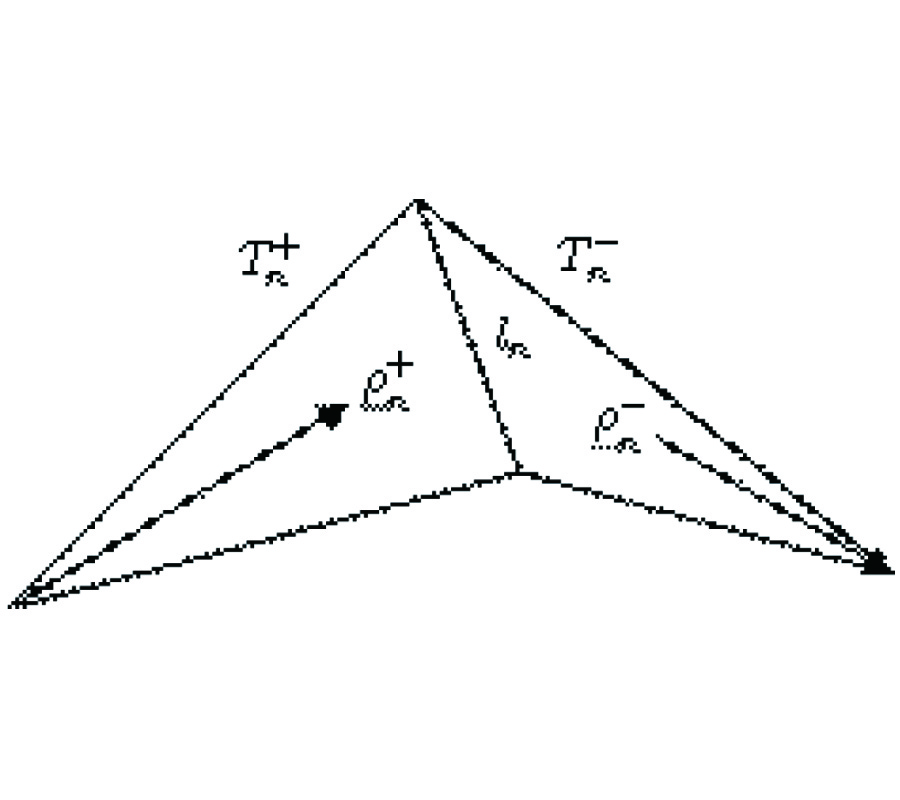
In this paper, we present four different formulations for the analysis of electromagnetic scattering from arbitrarily shaped three-dimensional (3-D) homogeneous dielectric body in the frequency domain. The four integral equations treated here are the electric field integral equation (EFIE), the magnetic field integral equation (MFIE), the combined field integral equation (CFIE), and the PMCHW (Poggio, Miller, Chang, Harrington, and Wu) formulation. For the CFIE case, we propose eight separate formulations with different combinations of expansion and testing functions that result in sixteen different formulations of CFIE. One of the objectives of this paper is to illustrate that not all CFIE are valid methodologies in removing defects, which occur at a frequency corresponding to an internal resonance of the structure. Numerical results involving the equivalent electric and magnetic currents, far scattered fields, and radar cross section (RCS) are presented for three canonical dielectric scatterers, viz. a sphere, a cube, and a finite circular cylinder, to illustrate which formulation works and which does not.