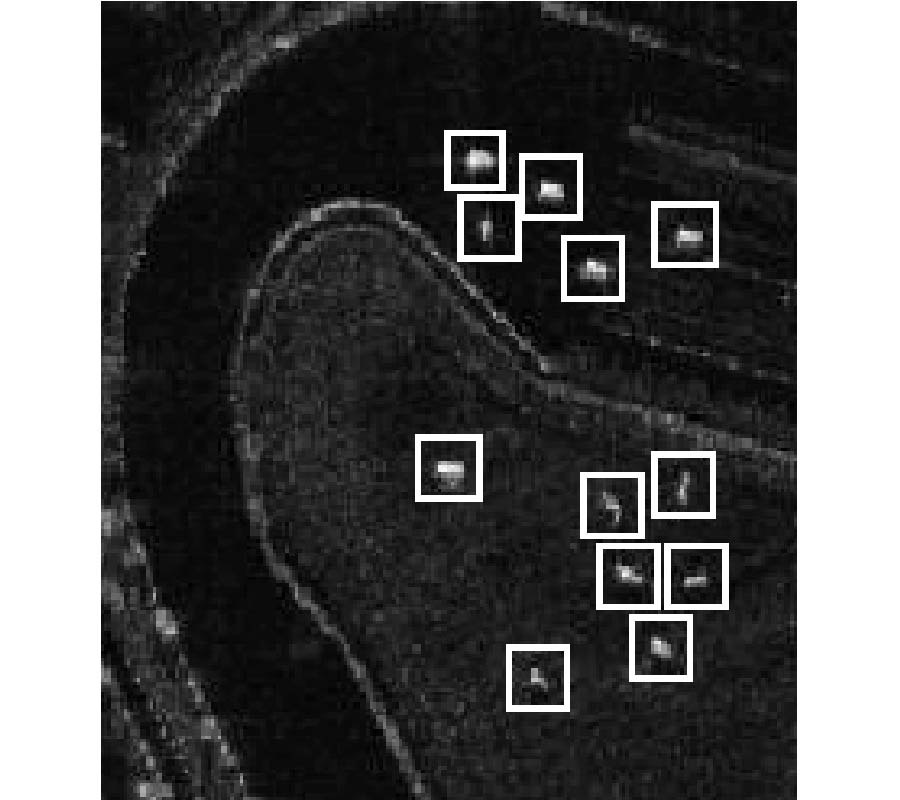
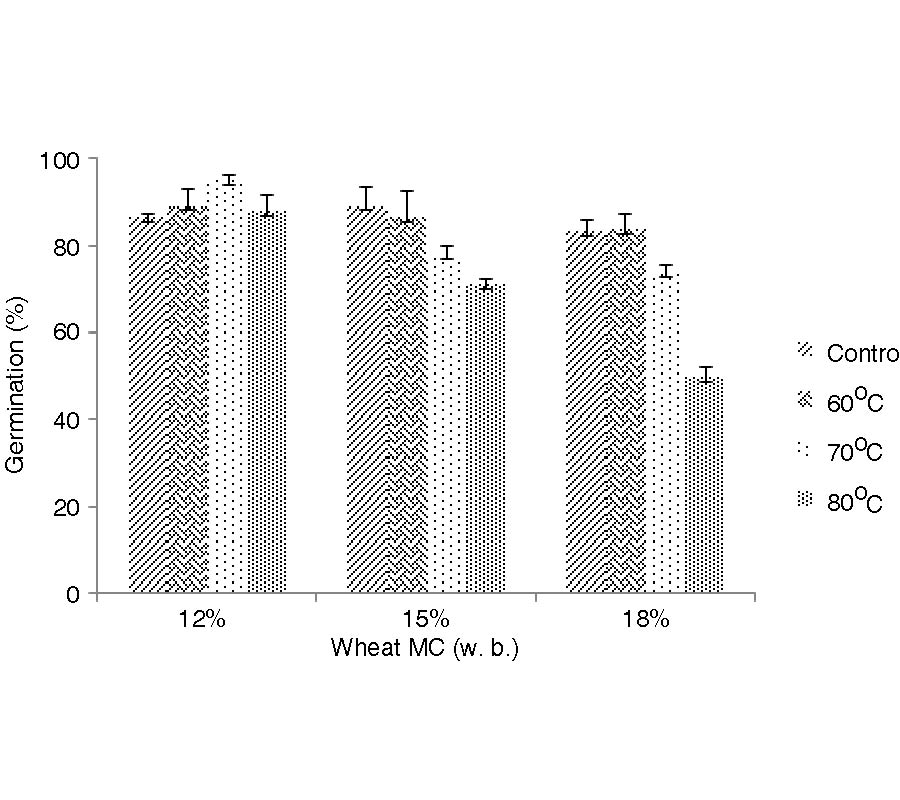
Elimination of Cruptolestes Ferrungineus S. in Wheat by Radio Frequency Dielectric Heating at Different Moisture Contents
Bijay Shrestha,
Daeung Yu and
Oon-Doo Baik
Radio frequency (RF) dielectric heating was tested to control Cryptolestes ferrungineus S. in the bulk wheat samples (ca.152 g, dia. = 50 mm, ht.= 100 mm) at the MCs (%, w. b.) of 12, 15, and 18 using a pilotscale RF heater (1.5 kW, 27.12MHz) in the batch mode. When the temperature of the hottest spot (geometric center) of the sample, TH was at 80°C, all the adult insects were found dead at the cold spots, near bottom-wall, at 50.7°C to 56.0°C depending up on the wheat MCs. The temperatures of the insect-slurries higher than that of the bulk wheat by 0.8°C to 15.1°C indicated the selective heating of the insects. The mortalities of adult insects were almost constant within the quarantine period, QP1 (5 wk). The elapsed time during QP1 had a significant effect only on the insects' mortalities with the wheat at 12% MC. The wheat MC had only marginal significance on the absolute mortalities of insects. The larvae were completely destroyed at temperatures between 55°C and 60°C. The complete mortality of all life stages (eggs, larvae, pupae, and adults) of the insect was achieved at TH = 80°C without any emergence of the insects during QP2 (8 wk). The RF treatment enhanced the germination of the wheat kernels at 12% MC while it was decreased by 2% to 33% depending up on the wheat MC, and the treatment temperature. Temperature had no significant effect on the falling numbers, and the yields of flour, bran, and shorts, and the peak-bandwidth and the MC of the wheat, and the flour protein values. The means of the mixing-development-time deferred from the controls mostly for the wheat at 15% MC and TH = 70°C, and 18% MC and TH = 70°C and 80°C. The mean-peak-height and the color values varied between 4% and 16%, and 3% and 6% off the controls depending up on the temperatures. The uniform temperature of 60°C should be enough to control all life stages of the insect completely with a little or no changes in the important product quaities and germination of the wheat at MCs safe for the storage. Future research mainly focused on better estimation of the insect-to-grain electric field intensities is essential.