Properties of Anisotropic Photonic Band Gaps in Three-Dimensional Plasma Photonic Crystals Containing the Uniaxial Material with Different Lattices
Hai Feng Zhang,
Shaobin Liu and
Xiang-Kun Kong
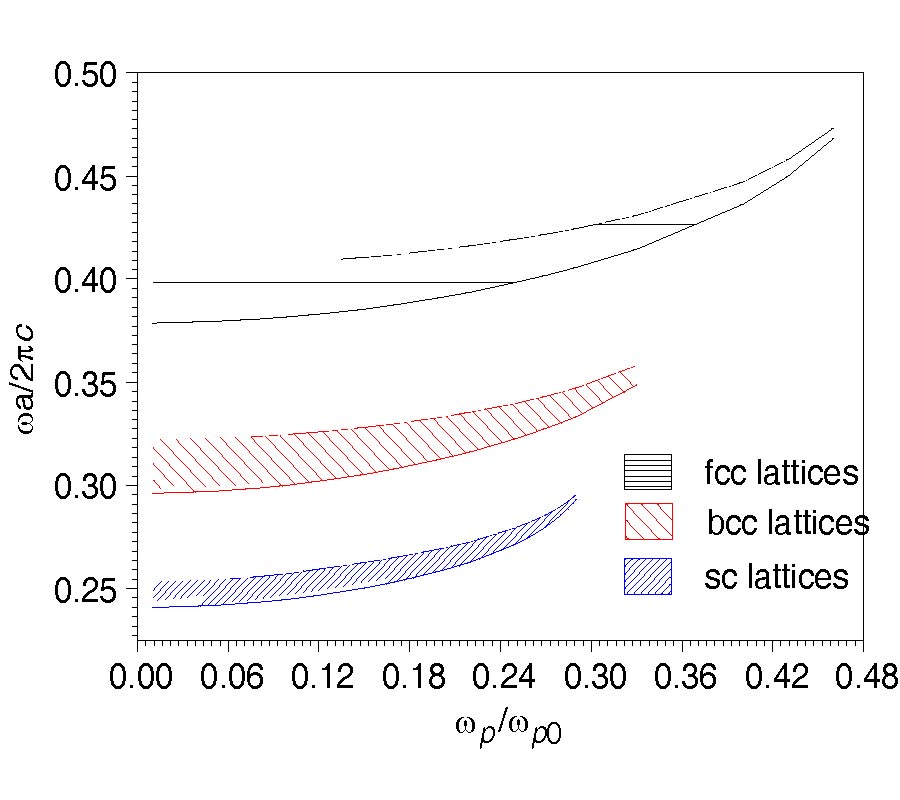
In this paper, the properties of anisotropic photonic band gaps (PBGs) in three-dimensional (3D) nomagnetized plasma photonic crystals (PPCs) composed of anisotropic dielectric (the uniaxial material) spheres immersed in uniform nomagnetized plasma background with various lattices including the diamond, face-centered-cubic (fcc), body-centered-cubic (bcc) and simple-cubic (sc) lattices, are theoretically investigated by the plane wave expansion (PWE) method. The equations for calculating the anisotropic PBGs in the first irreducible Brillouin zone are theoretically deduced. The anisotropic PBGs and a flatbands region can be obtained as the uniaxial material introduced into 3D PPCs. The PPCs with diamond lattices consisting of isotropic dielectric have the larger PBGs compared to PPCs doped by the uniaxial material since its low symmetry structure. Furthermore, the PPCs with fcc, bcc, sc lattices will not exhibit a complete PBG unless the uniaxial material is introduced. The influences of the ordinary-refractive index, extrordinary-refractive index, filling factor and plasma frequency external magnetic field on the properties of anisotropic PBGs for 3D PPCs with fcc, bcc, sc lattices are investigated in detail, respectively, and some corresponding physical explanations are also given. The numerical results show that the anisotropy can open partial band gaps in 3D PPCs with fcc, bcc, sc lattices, and the complete PBGs can be obtained compared to 3D PPCs doped by the conventional isotropic dielectric. It also is shown that the anisotropic PBGs can be tuned by the ordinary-refractive index, extrodinary-refractive index, filling factor and plasma frequency, respectively. The complete PBGs can be obtained by introducing the uniaxial material as 3D PPCs are with high-symmetry lattices. This also provides a way to design the tunable devices.