Multi-Physical Properties of Plasmonic Organic Solar Cells (Invited Paper)
Wallace C. H. Choy,
Wei E. I. Sha,
Xuanhua Li and
Di Zhang
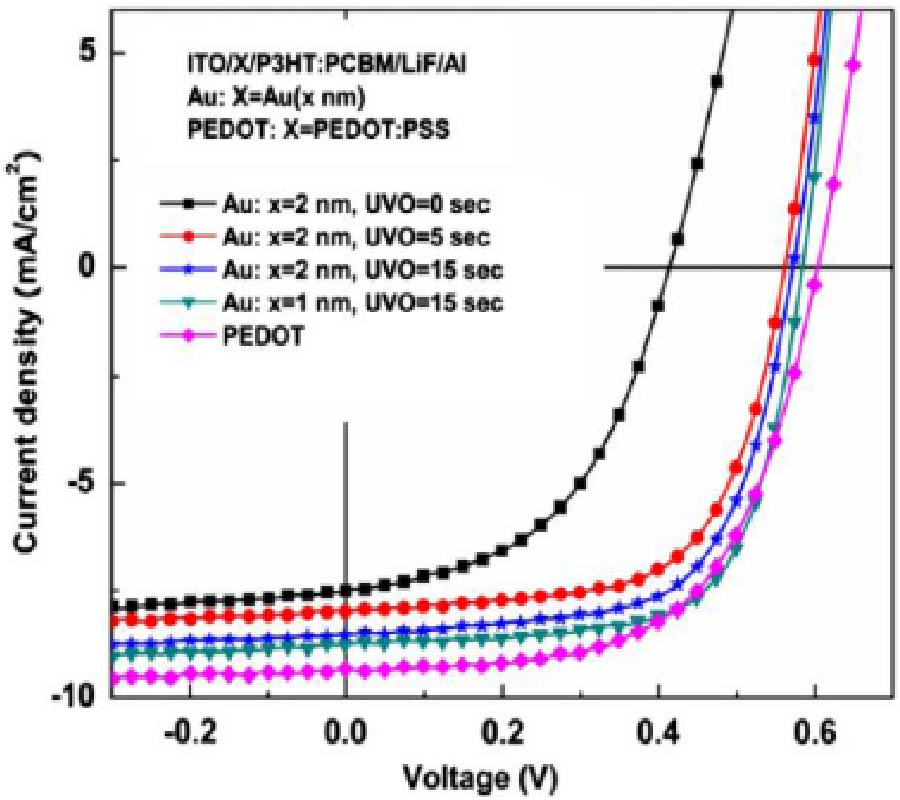
Organic solar cells (OSCs) have recently attracted considerable research interest. For typical OSCs, it is highly desirable to have optically thick and physically thin thickness for strong light absorption and efficient carrier collection respectively. In the meantime, most organic semiconductors have short exciton diffusion length and low carrier mobility [1-3]. As a consequence, the active layers of OSCs are generally thin with a thickness of few hundred nanometers to ensure the efficient extraction of carriers, hence limiting the total absorption of incident light. Optimizing both the optical and electrical (i.e. multi-physical) properties of OSCs is in demands for rationally designed device architectures. Plasmonic nanomaterials (e.g. metallic nanoparticles [4-6], nanorods [7, 8], nanoprisms [9, 10], etc.) have recently been introduced into different layers of multilayered solar cells to achieve highly efficient light harvesting. The multilayered solar cells structures commonly have active layer, carrier (electron and hole) transport layer and electrode (anode and cathode). Through the localized plasmonic resonances (LPRs) [11-16] from metallic nanomaterials, very strong near-fields will be generated, which can provide a large potential for enhancing optical absorption in the multilayered OSCs. Besides the optical effects, it has been reported that metallic nanomaterials can modify the morphology, interface properties as well as the electrical properties of OSCs which will significantly modify the performances of OSCs [17-23]. In this article, the effects of various optical resonance mechanisms and the theoretical studies of the multi-physical properties of OSCs will be reviewed. Meanwhile, the experimental optical and electrical effects of metallic nanomaterials incorporated in different layers of OSCs will be studied. The morphology and interface effects of metallic nanomaterials in the carrier transport layers on the performances of OSCs will also be described.