Multi-Band Antenna Array Based on Double Negative Metamaterial for Multi Automotive Applications
Abdulrahman Shueai Mohsen Alqadami,
Mohd Faizal Bin Jamlos,
Imtiaz Islam,
Ping Jack Soh,
Rizalman Mamat,
Khairil Anuar Khairi and
Adam Narbudowicz
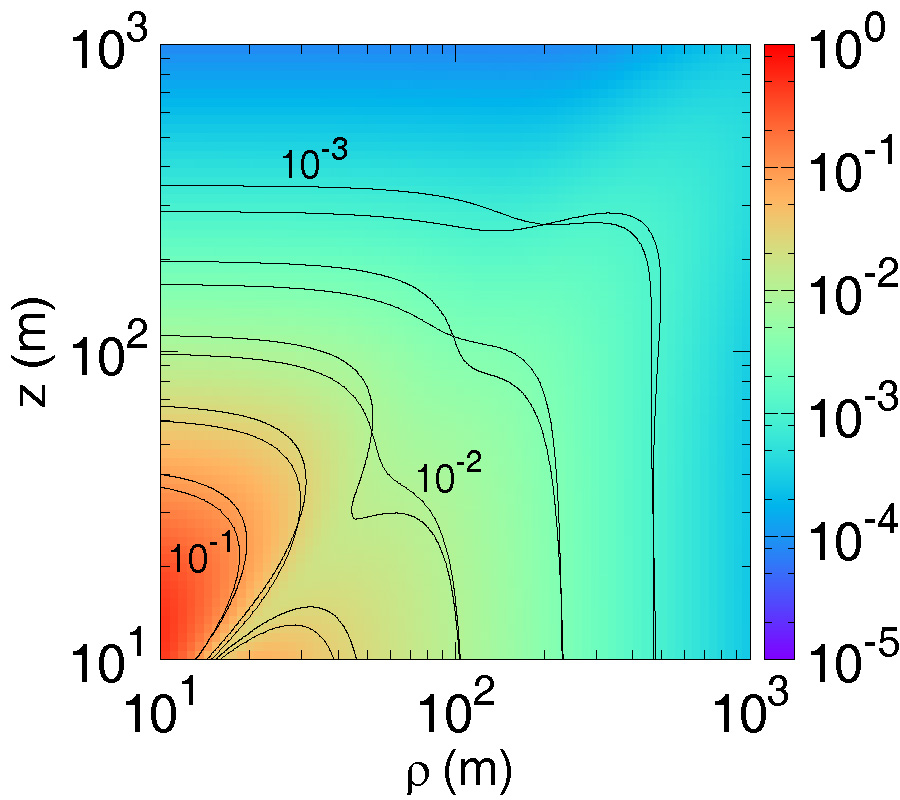
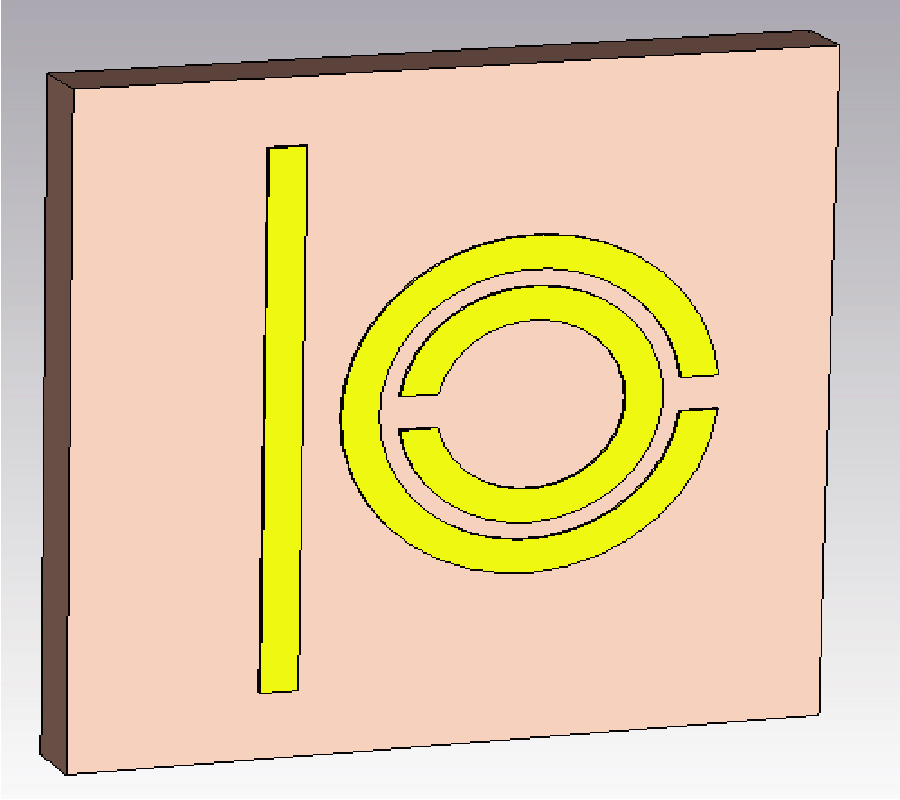
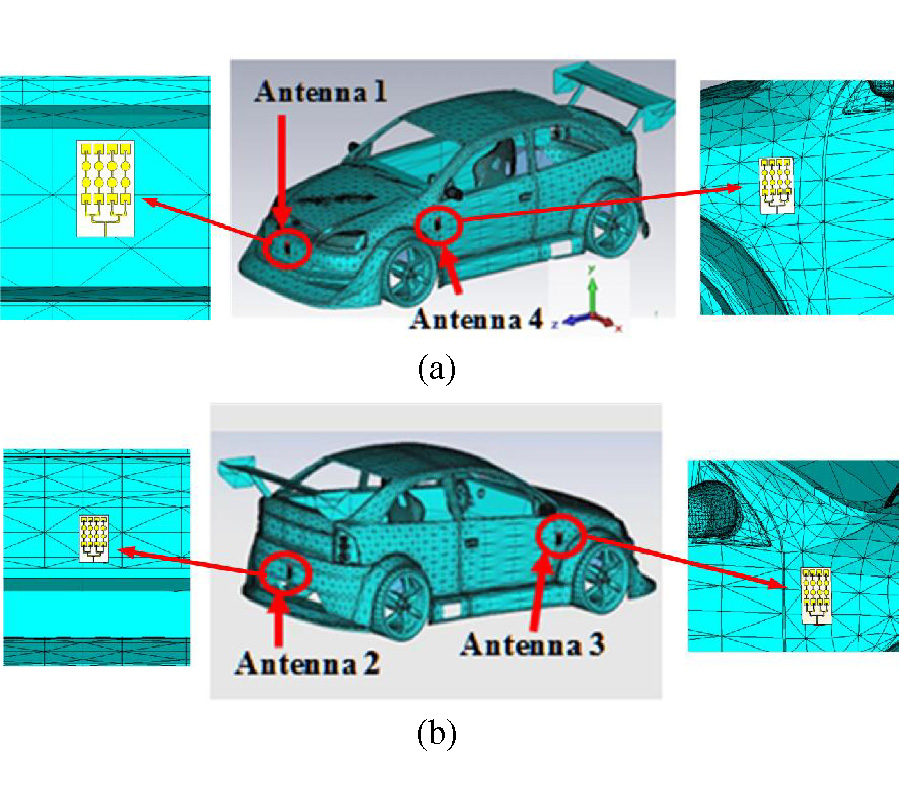
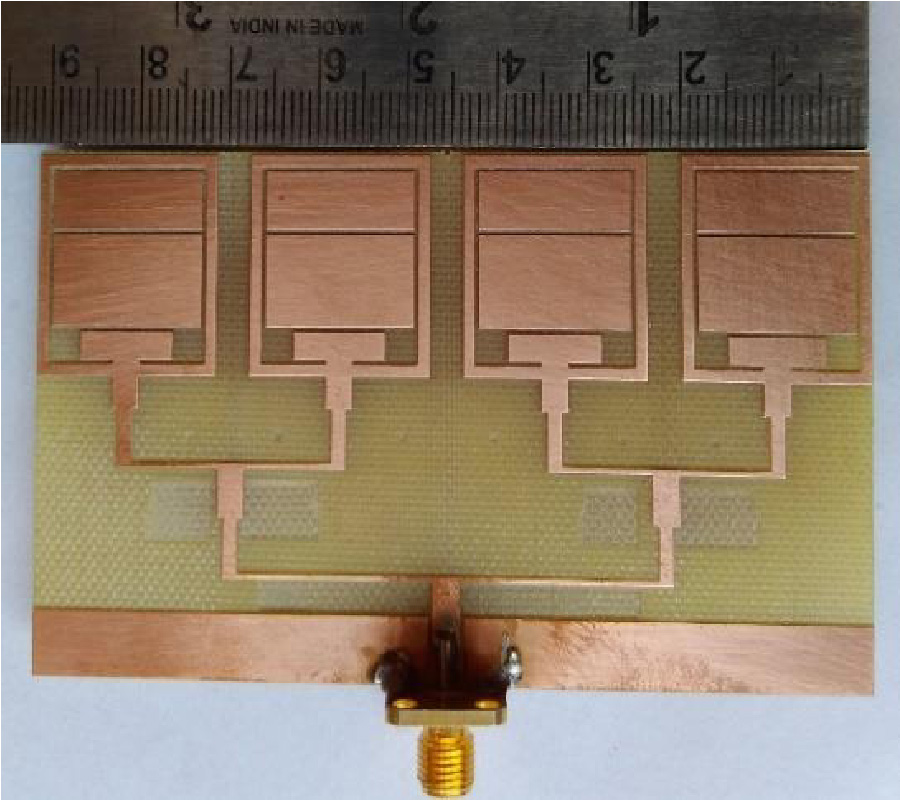
This paper presents a design of multi-band array antenna based on Double Negative Metamaterial (DNM) unit cells for multi-automotive applications. The antenna consists of 4×4 rectangular and circular radiating patches connected in series using microstrip lines and fed by a 50 Ω corporate microstrip line. An array of 4×6 wire loaded complementary spiral resonator (CSR) unit cells is placed on its reverse side to provide miniaturization and multiband features to the proposed design. The reflection coefficient (S11), mutual coupling, effective diversity gain (EDG), envelope correlation coefficient (ECC), and radiation patterns are evaluated for four elements of the proposed antenna placed in four different locations on the car body model. Simulations and measurements indicated that the proposed antenna features a low mutual coupling (<-34 dB), low ECC (<0.0001), high EDG (>9.99), high efficiency (72%-95%), and low on-car detuning over the operating frequency bands. The proposed antenna covers five bands; 1.99 GHz to 3.03 GHz, 5.15 GHz to 6.369 GHz, 7.67 GHz to 7.99 GHz, 9.91 GHz to 10.23 GHz, and 11.79 GHz to 12.2 GHz. The performance of ECC between four antennas on car body has been investigated in different cases of isotropic, indoor, and outdoor. The metallic effect on antennas performance also has been investigated by evaluating the mutual coupling and transmission coefficient between two antennas served as transmitter and receiver with presence of car body. The results show transmission coefficient of proposed DNM antenna with metallic presence almost identical to free space across desired frequency bands. With all capabilities mentioned the antenna has potential for WiFi/WiMAX, Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V), transportable earth exploration satellite, military requirement for land vehicles, and earth stations on vessels applications.