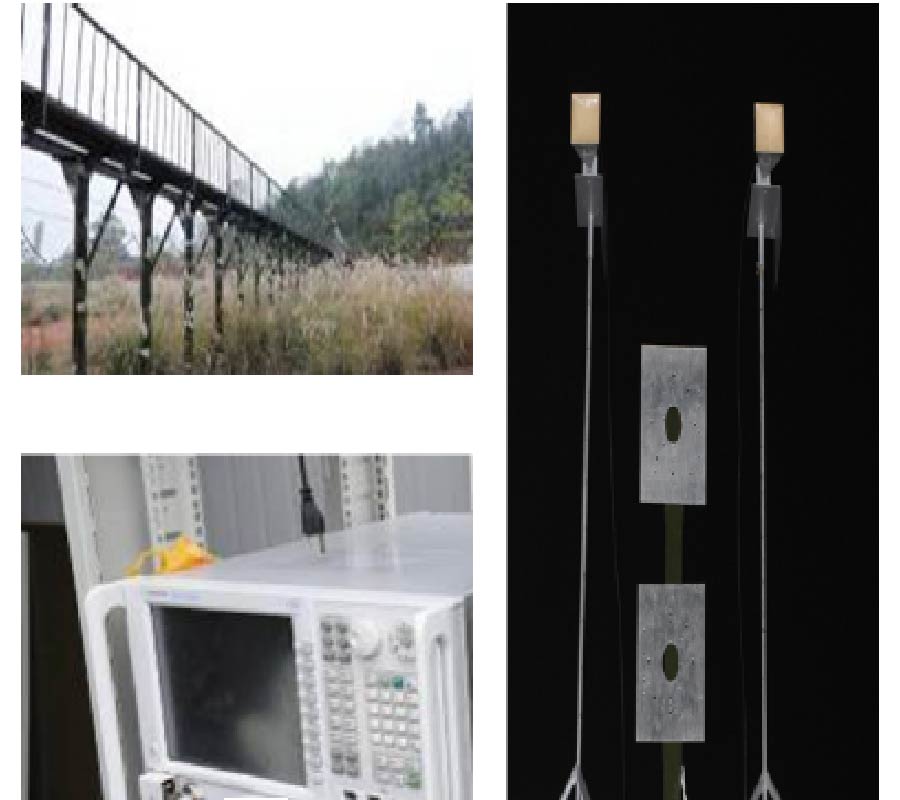
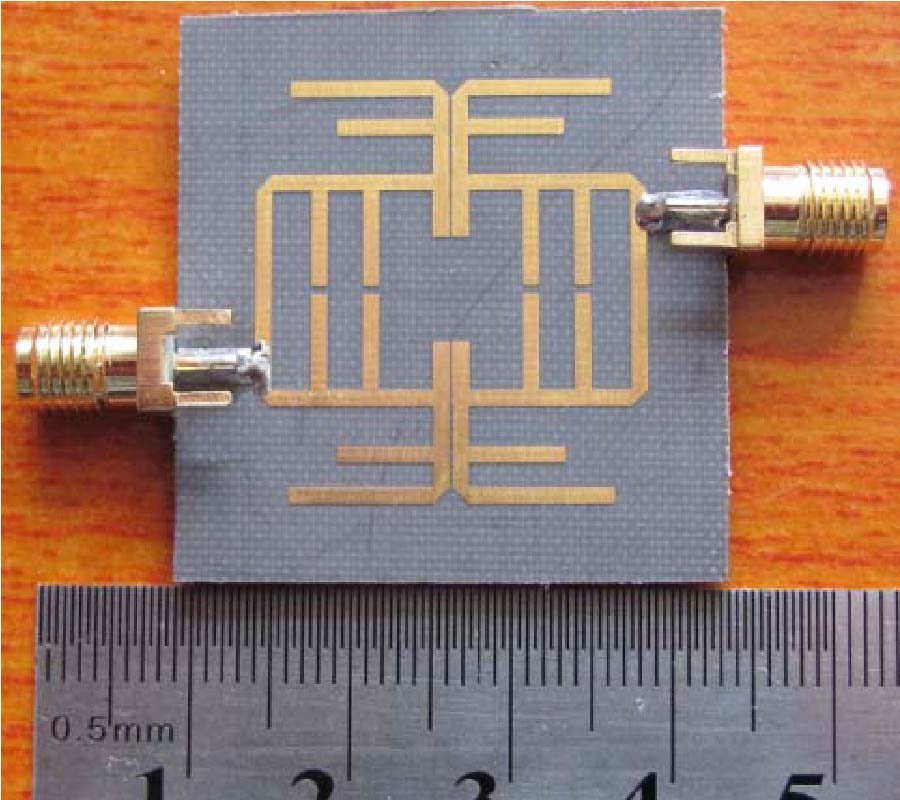
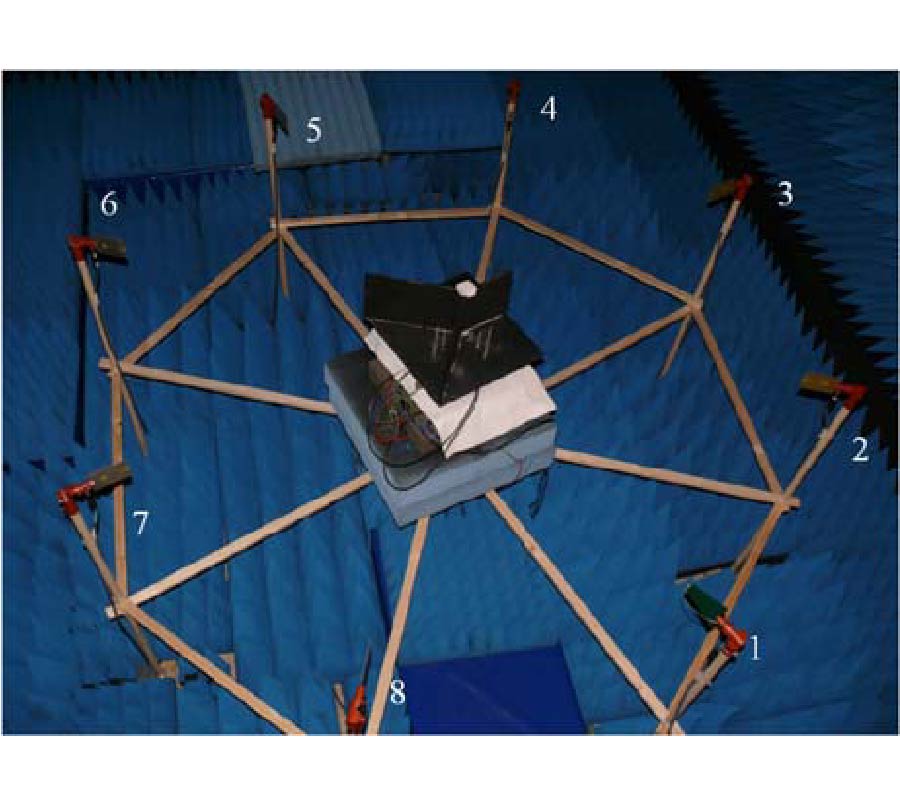
Electronically Reconfigurable Beam Steering Antenna Using Embedded RF PIN Based Parasitic Arrays (Erppa)
Thennarasan Sabapathy,
Mohd Faizal Bin Jamlos,
Raad Badlishah Ahmad,
Muzammil Jusoh,
Mohd Ilman Jais and
Muhammad Ramlee Kamarudin
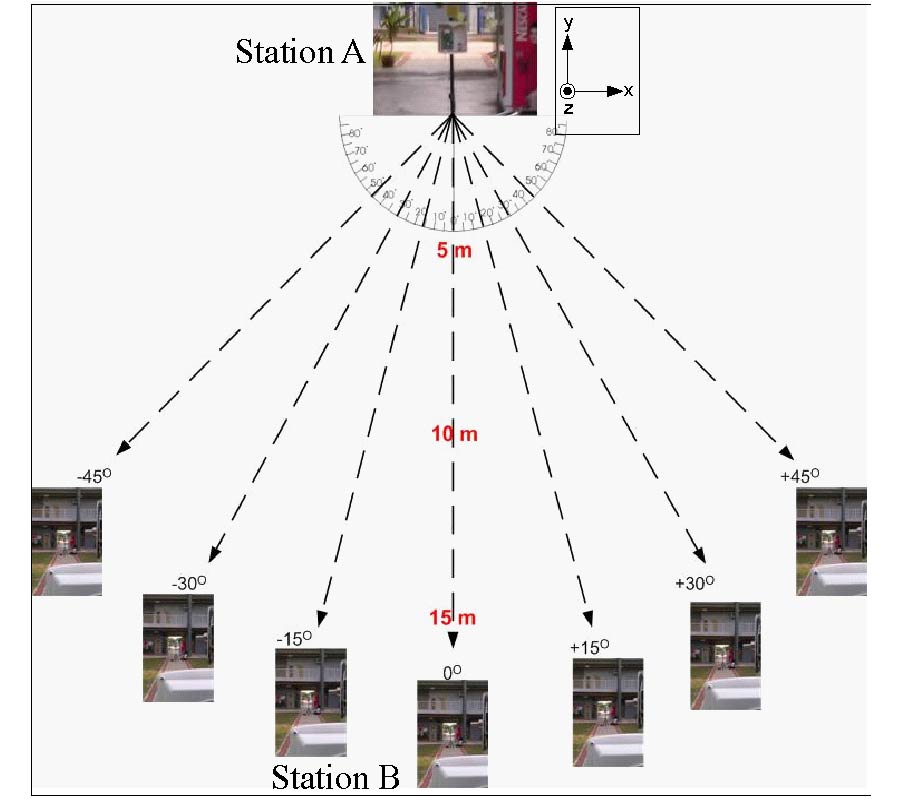
In this paper, an electronically reconfigurable beam steering antenna using embedded RF PIN switches based parasitic array (ERPPA) is proposed for modern wireless communication systems that operate at 5.8 GHz frequency. In the proposed antenna, a single driven element is fed by a coaxial probe, while each of the two parasitic elements is integrated with an RF PIN switches that embedded inside the substrate. In the conventional reconfigurable antennas, the RF PIN switches are mounted on narrow slots created on the top or bottom layer of the radiator/parasitic elements, which could lead to the dimensional changes of the antenna and degrade the performance in terms of beam steering and return loss. However, this research proposes an exclusive solution where the RF PIN diodes at parasitic elements are embedded inside the substrate thus no additional slots have to be created to mount the SMCs on the antenna. In this regard, the proposed antenna is highly competent to eliminate the intermodulation effect generated by the RF PIN diodes and the other passive elements associated with the PIN diodes. In this research, extensive investigations revealed that the parasitic element dimension and the selection of RF PIN switches significantly influence the antenna's beam steering capability. Adopting certain ON/OFF condition of the embedded RF switches, three beam-steering angles of -30°, 0° and +30° are achieved in the xz-plane, with measured peak gains at θ = -30°, 0° and +30° are 6.5 dBi, 6.5 dBi and 4.9 dBi, respectively. The fabricated antenna with Taconic substrate provides a good agreement with the simulation result. Furthermore, the performance of ERPPA is further tested by outdoor measurement using a wireless bridging system to verify the functionality of the designed antenna at the angles of -45°, -30°, -15°, 0°, 15°, 30° and 45°. The analysis with the switched diversity combining scheme has demonstrated that a maximum diversity gain approximately of 12 dBi is offered by the proposed antenna. With a compact dimension of 32 mm by 76 mm, the proposed antenna is a potential candidate in point-to-point wireless applications such as WIFI application.