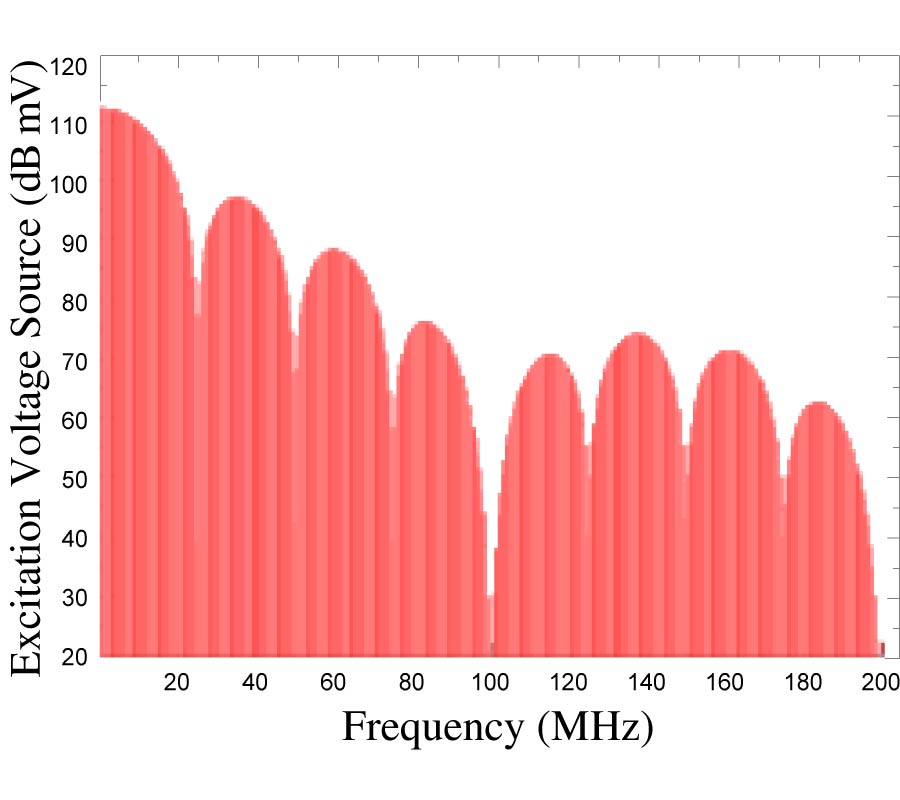
Gradual Thinning Synthesis for Linear Array Based on Iterative Fourier Techniques
Xin-Kuan Wang,
Yong-Chang Jiao and
Yan Yan Tan
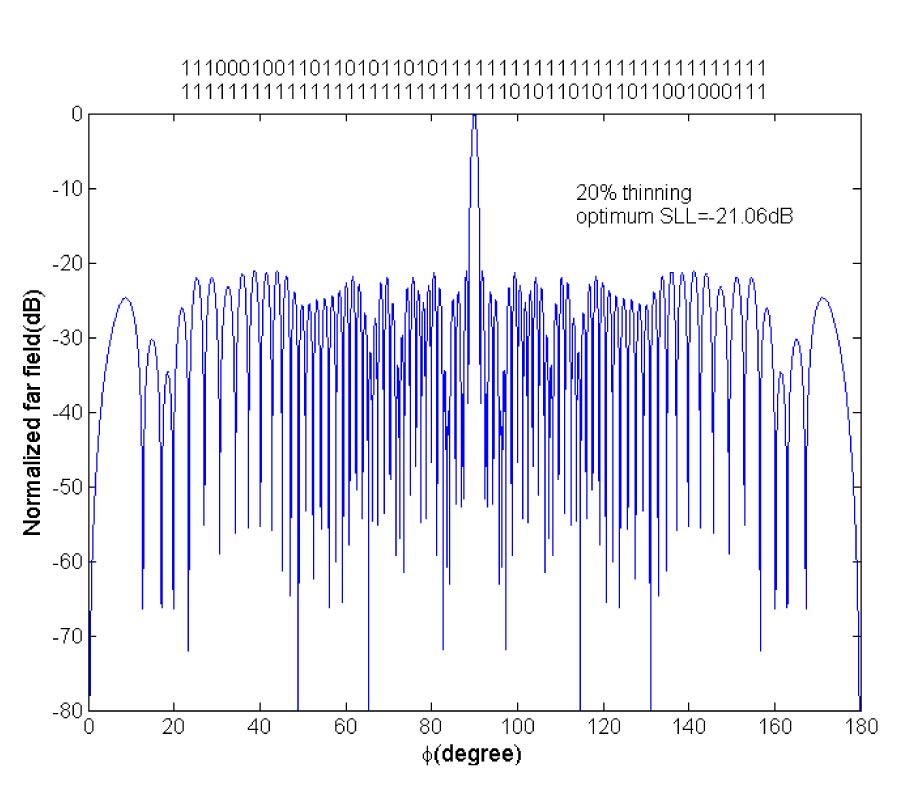
In this paper, a modified iterative fourier technique (MIFT) for thinning uniformly spaced linear arrays featuring a minimum sidelobe level as well as narrow beam is presented. Since IFT is a thinning procedure which has to be performed many trial times with different initial element distributions to get the optimum solution, it is, to some extent, time consuming. Moreover, in each trial of IFT, the number of iterations is usually low, which makes the method tend to be trapped in local solution even with a large number of trials. Therefore, the similar procedures for both MIFT and IFT are to derive the element excitations from the prescribed array factor using successive forward and backward Fourier transforms, and array thinning is accomplished by setting the amplitudes of a predetermined number of the largest element excitations to unity while the others to zero during each iteration cycle. Furthermore, in MIFT, based on the idea of gradual thinning which is inspired by perturbation theory, an adaptively changed fill factor is proposed to modify IFT with the purpose of accelerating computational speed and facilitating convergence. The immediate result caused by this modified fill factor can be embodied in two points. One point is that unlike the random number of iterations contained in different trials of IFT, the number of iterations in all trials of MIFT is a fixed value and only predetermined by the array inherent features (symmetrical or asymmetrical) and fill factor. Therefore, sufficient iterations are ensured in each trial to effectively help the algorithm avoid trapping. The other point is that when MIFT is performed, the array elements are gradually truncated, which maintains the most useful element excitations while maximally excludes the bad excitations, so that the optimum solution could be obtained through only a small number of trials and thereby substantially save computational cost. The effectiveness of MIFT will be demonstrated for various linear arrays and compared with the published reports.