Five-Zone Propagation Model for Large-Size Vehicles Inside Tunnels
Ke Guan,
Zhangdui Zhong,
Bo Ai,
Ruisi He and
Cesar Briso-Rodriguez
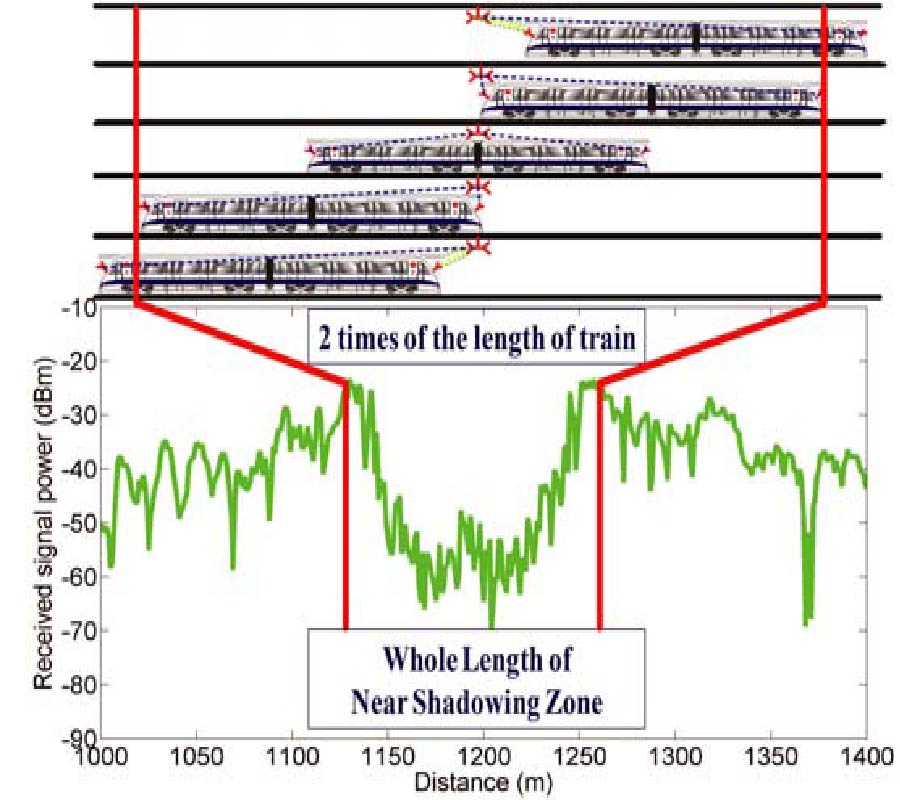
An accurate characterization of the wave propagation inside tunnels is of practical importance for the design of advanced communication systems. This paper presents a five-zone propagation model for large-size vehicles inside tunnels. Compared with existing models, the proposed model considers the influence of the large size of the vehicle, and covers all propagation mechanism zones and their dividing points. When a large-size vehicle is passing the transmitter, the received power suffers a deep fading as the direct wave is blocked by the vehicle itself. This zone is called the near shadowing zone. Then, when the vehicle has moved past the transmitter, the line of sight is recovered. If the vehicle is still close to the transmitter, the free space propagation zone starts. Then, as the distance increases, the vehicle enters the multi-mode propagation zone, where higher order modes are significant. Further away, when high order modes are greatly attenuated, guided propagation is stabilized. Finally, when the vehicle is extremely far from the transmitter, the waveguide effect vanishes because of the attenuation of reflected rays. Two sets of measurements are employed to validate the model. Results show good agreement, and therefore, the model presents an effective way to predict the propagation inside tunnels for large-size vehicles.