2023-12-31 Latest Published
By Firoz Kanti Borah
Leung Tsang
Edward J. Kim
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 178, 129-147, 2023
Abstract
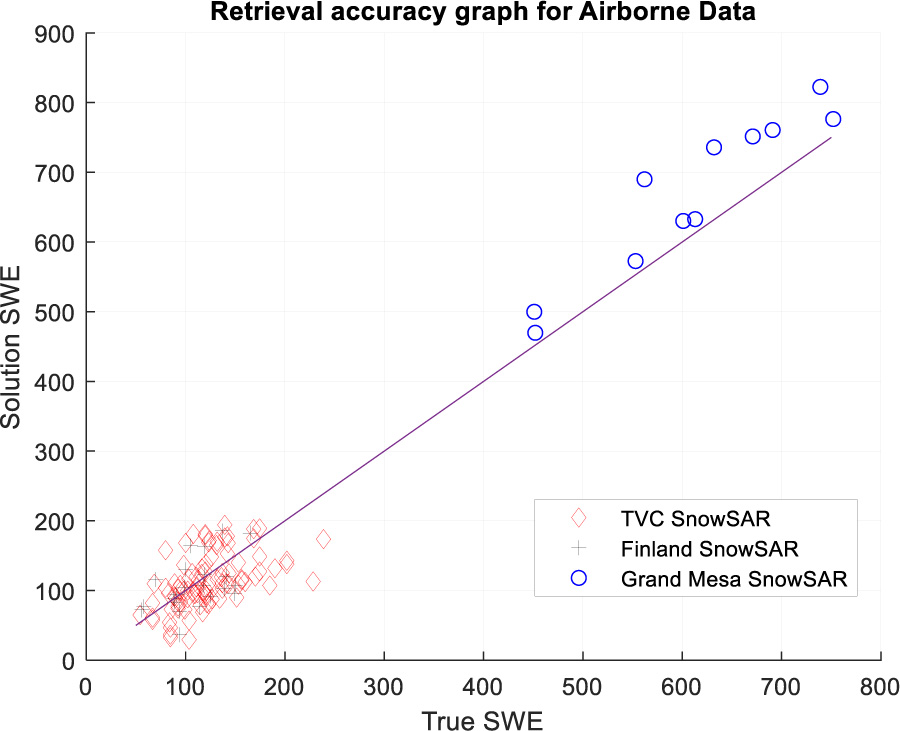
In this paper, we develop two new algorithms for snow water equivalent (SWE) retrieval based on the volume scattering snow at X (9.6 GHz) and Ku (17.2 GHz). Significantly, neither algorithm requires a prior on grain size or on scattering albedo. The two algorithms are based on modifications of the previous algorithm published in our previous two papers (Zhu et al. 2018, 2021). The physical model is the bi-continuous DMRT model, and a parametrization is carried out over a look-up table of DMRT results. The parameterized model gives the X and Ku band co-polarization backscatter as a pair of equations in terms of two parameters SWE and scattering albedo at X band (ωX). By directly inverting the pair of equations for, σX (SWE, ωX) and σKu (SWE, ωX), we show that there are at most a pair of solutions which have SWE values that are far apart in most cases, facilitating identification of the correct solution. The first algorithm described in this paper, labelled an algebraic algorithm, uses inversion alone and does not employ a cost function. The proposed algebraic algorithm is validated with multiple airborne data sets and three years of tower-based snow observations. The robustness of the no-prior approach was validated with the airborne observations, by using a prior SWE value that is intentionally far (75% different) from the true SWE. For the validation using tower-based data, three years of observations from the NoSREx experiment in Sodankyla, Finland were used in which the previous SWE result helps to correctly choose between the two solutions. The second cost function-based algorithm finds the SWE and ωX pair which minimizes the difference between the observed volume scattering σX,obs and σKu,obs and the model-predicted volume scattering σX,mod and σKu,mod. The cost function uses prior information on SWE, also based on a time series starting with zero/low SWE. NoSREx data is used to show results from this approach. The new algorithm combined with time series eliminates needs of ancillary information of SWE and grain sizes, making the algorithm useful for level-2 products of a satellite mission.