A Non-Destructive Technique for Asphalt Compaction Measurement Using Dual-Ring Resonator Sensor
Mohammed K. Abbas,
Raaed Thaaban Hammed,
Ali J. Salim and
Aduwati Sali
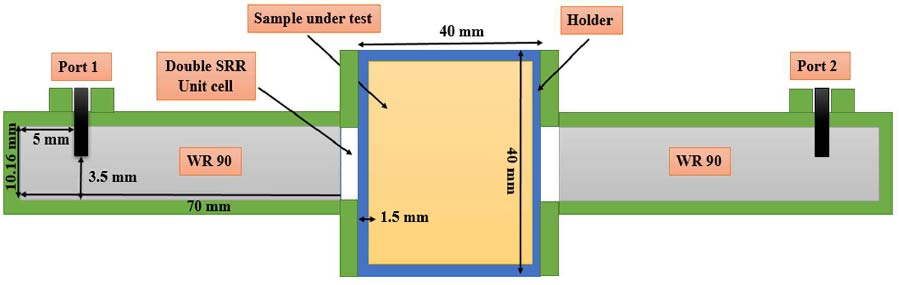
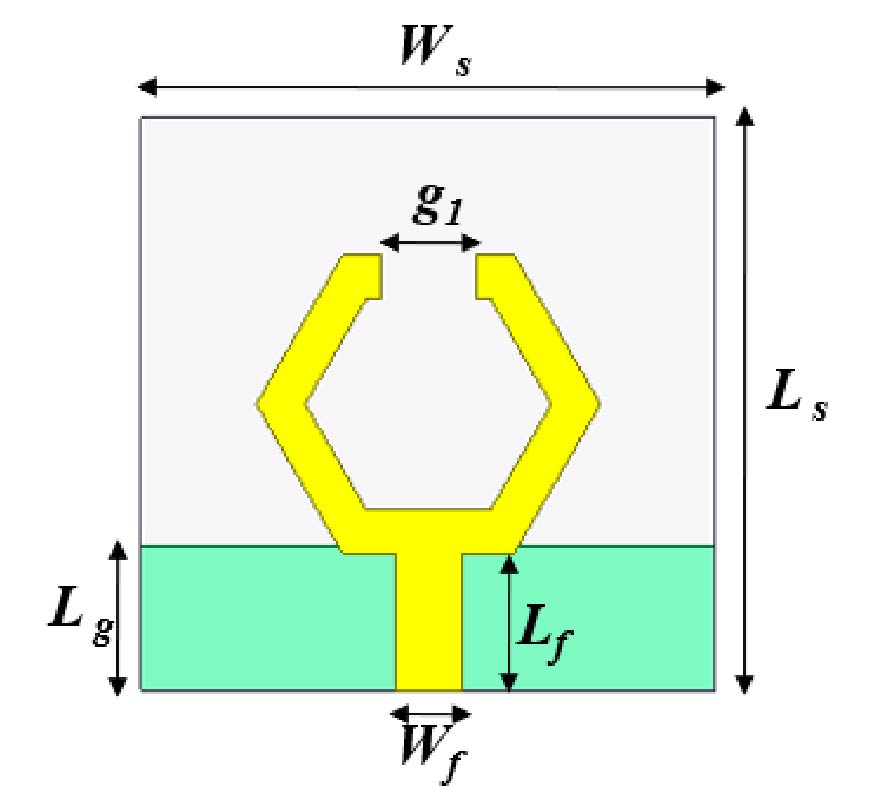
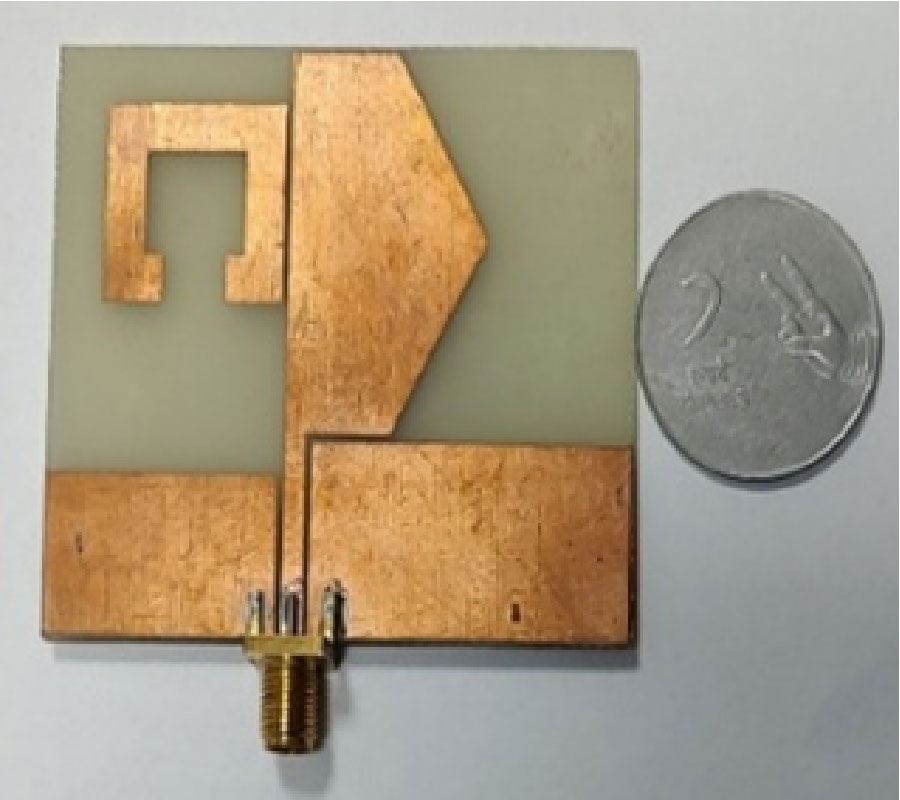
Traditional ways of measuring compaction of asphalt, which involve destructive coring, are labor-intensive, time-consuming, and cause permanent damage to the road. This paper presents a non-destructive alternative using a dual-ring resonator sensor (DRRS) integrated with a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) to evaluate asphalt compaction. The sensor design takes advantage of the electric field that forms between the first and second rings. This field can penetrate the asphalt layer to a depth of up to 50 mm and responds to changes in compaction levels. By putting asphalt samples of different densities on the sensor and measuring scattering parameters (S-parameters), changes in the resonant frequency are shown. These shifts were correlated with asphalt's physical properties through empirical equations. The results showed that the resonant frequency and the reflection coefficient (S11) were -25.5 dB and 1.38 GHz, respectively, at a 75% compaction level. The frequency changed to 1.17 GHz at 100% compaction, and S11 was -17.6 dB. Increasing the compaction of asphalt makes the air gaps in the material smaller, which makes its permittivity higher. Calibration was performed to mitigate the influence of temperature on permittivity measurements, thereby improving compaction. Overall, this method provides a fast, precise, and non-destructive way to check the quality of asphalt, significantly enhancing road construction and maintenance processes.