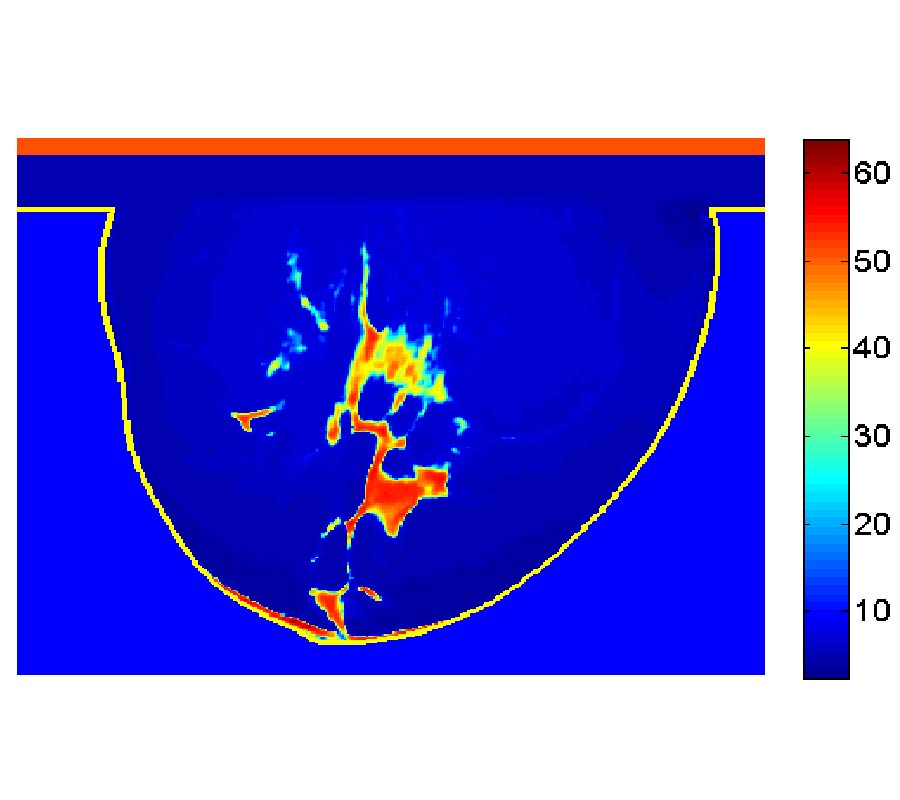
Absolute Imaging of Low Conductivity Material Distributions Using Nonlinear Reconstruction Methods in Magnetic Induction Tomography
Bachir Dekdouk,
Christos Ktistis,
David W. Armitage and
Anthony J. Peyton
Magnetic Induction Tomography (MIT) is a newly developing technique of electrical tomography that in principle is able to map the electrical conductivity distribution in the volume of objects. The image reconstruction problem in MIT is similar to electrical impedance tomography (EIT) in the sense that both seek to recover the conductivity map, but differ remarkably in the fact that data being inverted in MIT is derived from induction theory and related sources of noise are different. Progress in MIT image reconstruction is still limited, and so far mainly linear algorithms have been implemented. In difference imaging, step inversion was demonstrated for recovering perturbations within conductive media, but at the cost of producing qualitative images, whilst in absolute imaging, linear iterative algorithms have mostly been employed but mainly offering encouraging results for imaging isolated high conductive targets.
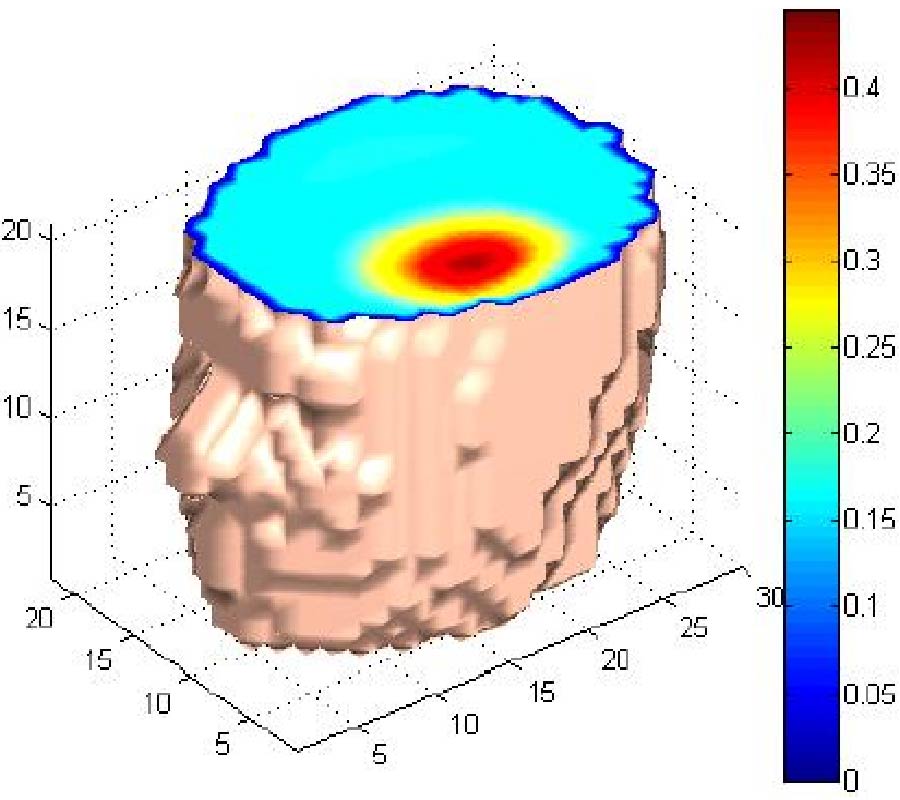
In this paper, we investigate the possibility of absolute imaging in 3D MIT within a target for low conductivity application (σ < 5 Sm-1). For this class of problems, the MIT image reconstruction exhibits non-linearity and ill-posedness that cannot be treated with linear algorithms. We propose to implement for the first time in MIT two effective inversion methods known in non-linear optimization as Levenberg Marquardt (LMM) and Powell's Dog Leg (PDLM) methods. These methods employ damping and trust region techniques for controlling convergence and improving minimization of the objective function. An adaptive version of Gauss Newton is also presented (AGNM), which implements a damping mechanism to the regularization parameter. Here, the level of penalty is varied during the iterative process. As a comparison between the methods, different criteria are examined from image reconstructions using the LMM, PDLM and AGNM. For test examples, volumetric image reconstruction of a perturbation within homogeneous cylindrical background is considered. For inversion, an independent finite element FEM software package Maxwell by Ansys is employed to generate simulated data using a model of a 16 channel MIT system. Numerical results are employed to show different performance characteristics between the methods based on convergence, stability and sensitivity to the choice of the regularization parameter. To demonstrate the effect of scalability of absolute imaging in MIT for more realistic problems, a human head model with an internal anomaly is used to produce reconstructions for different finer resolutions. AGNM is adopted here and employs the Krylov subspace method to replace the computationally demanding direct inversion of the regularized Hessian.