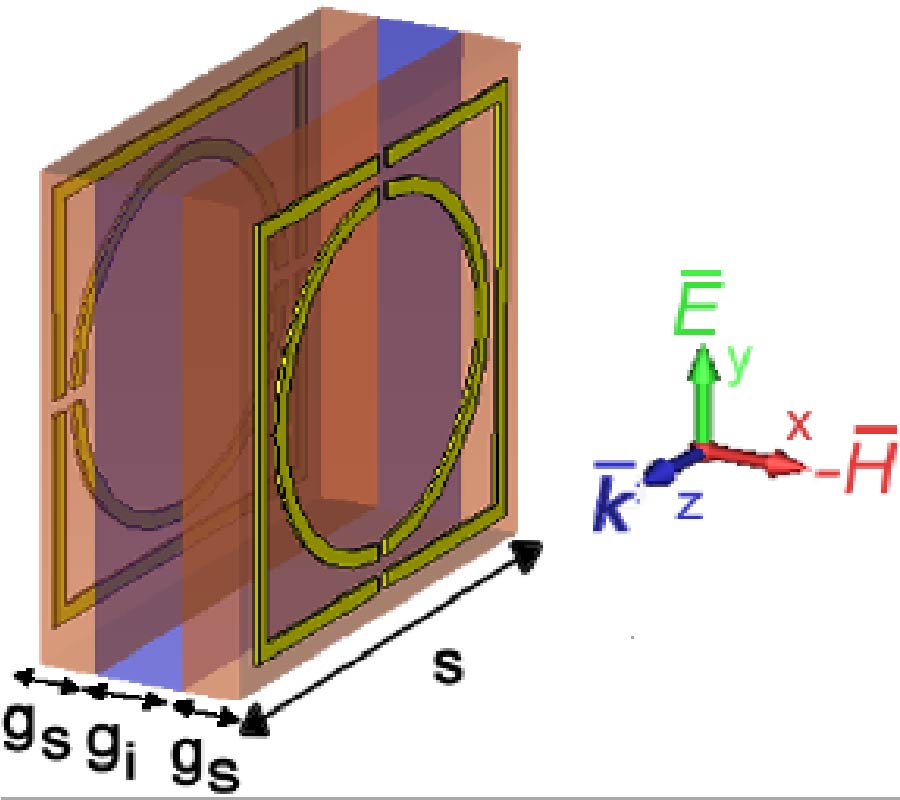
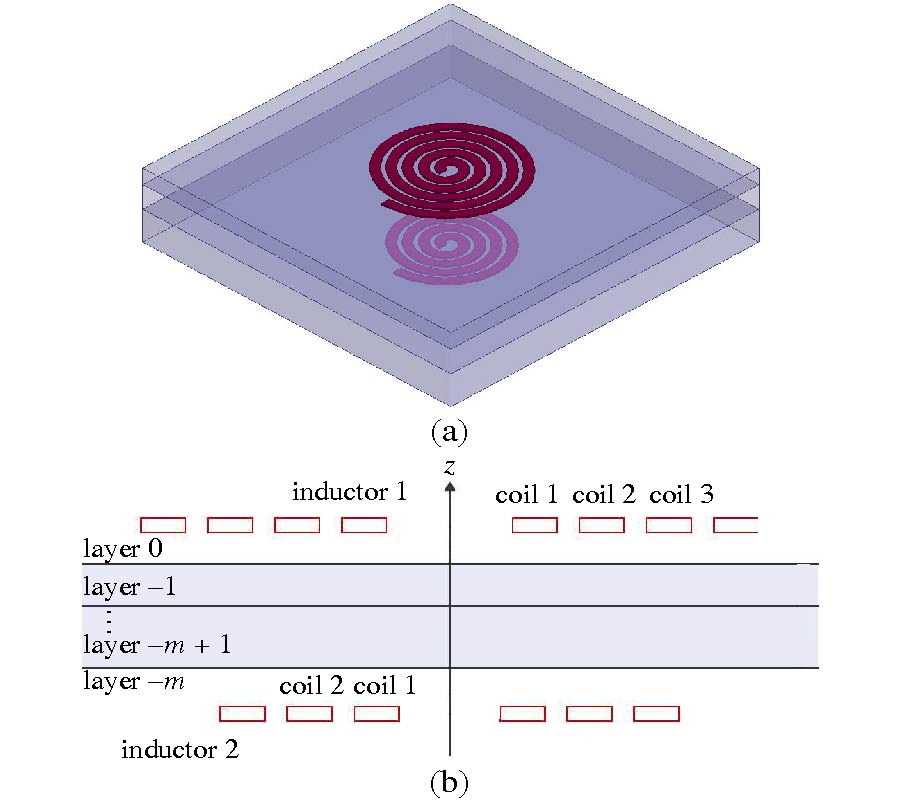
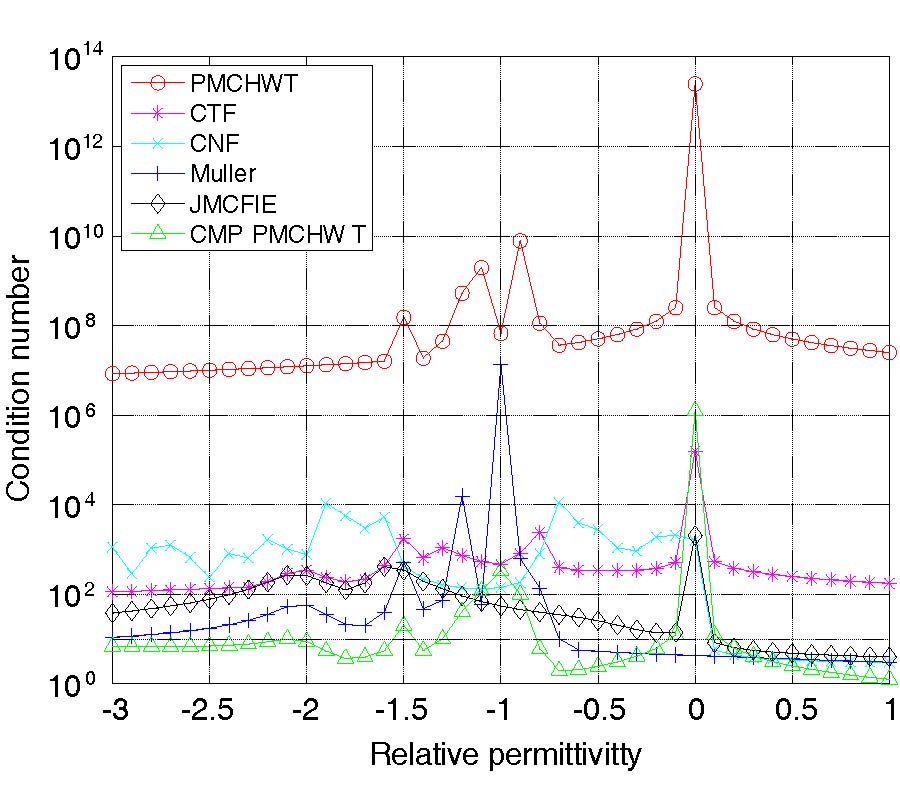
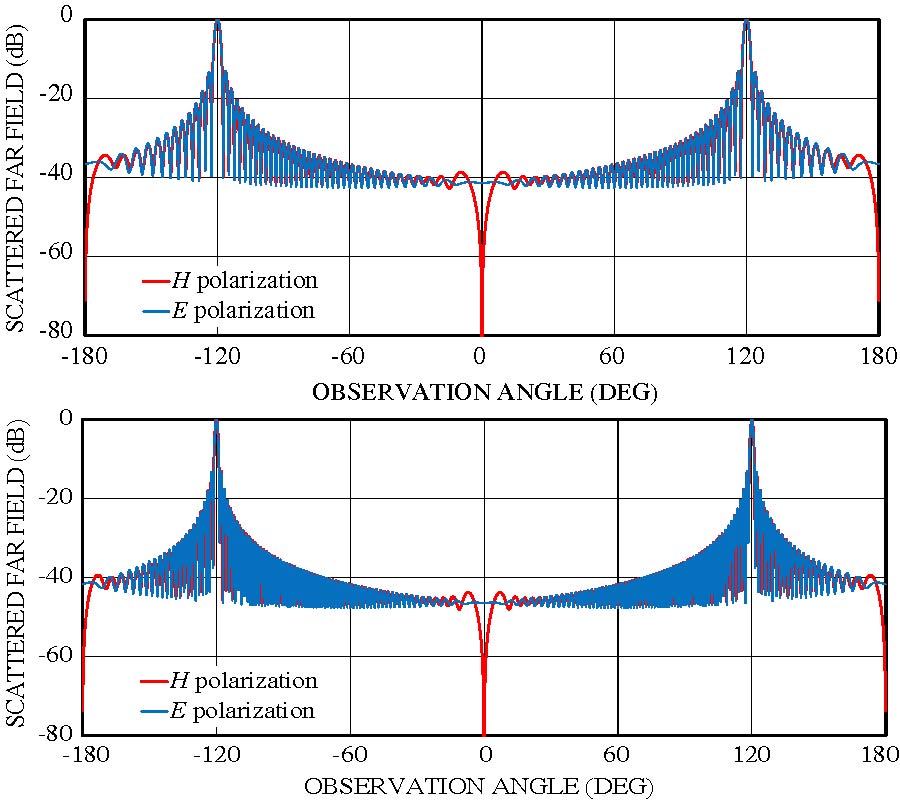
Casimir Force for Complex Objects Using Domain Decomposition Techniques
Phillip R. Atkins,
Weng Cho Chew,
Maokun Li,
Lin E. Sun,
Zu-Hui Ma and
Li Jun Jiang
A method for calculating the Casimir force between large, complex 3D objects is presented. Difficulties have previously arisen in broadband multiscale calculation using CEM methods. To expand the range of problems that can be calculated, we use an integral equation, domain decomposition method (DDM) and argument principle to derive the Casimir force formula. The broadband integral equation DDM, which is the augmented equivalence principle algorithm (A-EPA), allows for an efficient broadband solution of large, complex objects. A-EPA subdivides a complex problem into separate smaller subproblems that are later recombined into a reduced matrix. This yields a reduced number of unknowns for complex structures making them feasible with modest computer resources. We demonstrate the advantages of the A-EPA by simulating large, finite, 3D, unaligned corrugated plates, which have previously only been modeled approximately as infinite plates using 2D techniques.