Trapped Surface Wave and Lateral Wave in the Presence of a Four-Layered Region
Yi Hui Xu,
Wang Ren,
Liang Liu and
Kai Li
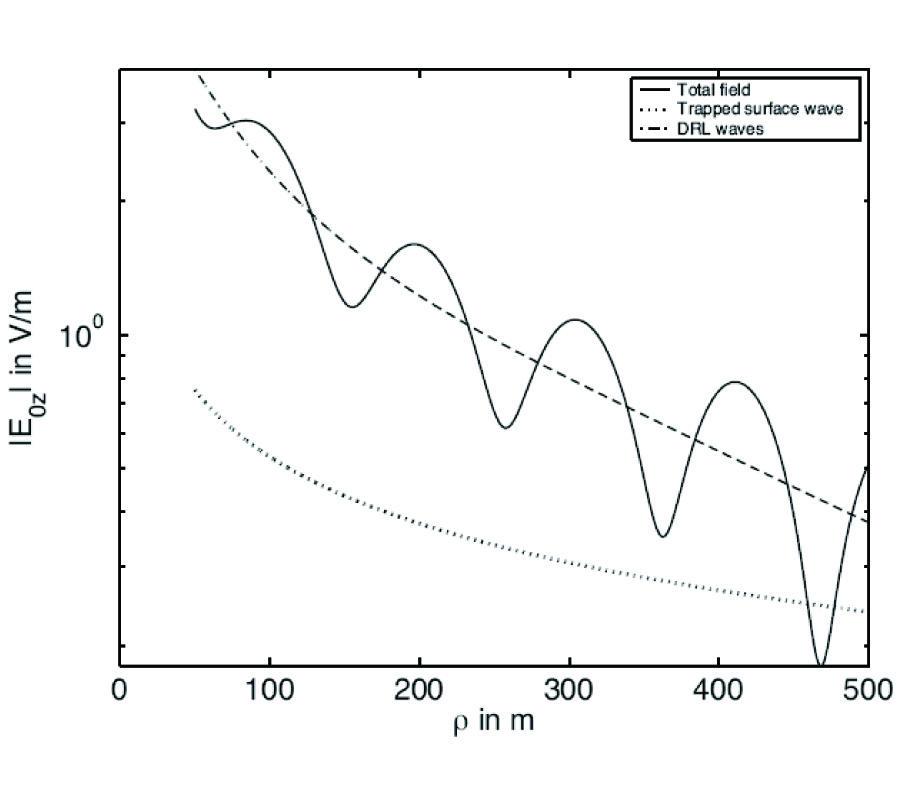
In this paper, propagation model considers the region as a perfect conductor, covered by the two layer dielectrics, and air above. Propagation of the electromagnetic field in the presence of a four-layered region is examined in detail when a vertical electric dipole and observation point are located in the air. Similar to the three-layered case, analytical results are found for the electromagnetic field, which includes four wave modes: a direct wave,an ideal reflected wave, trapped surface waves, and lateral waves. The wave number of the trapped surface wave, which is contributed by the sums of residues of the poles, is between the wave numbers k0 in the air and k2 in the lower dielectric layer. The lateral wave is evaluated by the integrations along the branch cut. Analysis and computations shows that the trapped surface wave play a major role in communication at large distance when both the source point and observation point are on or close to the boundary between the air and the upper dielectric layer.